The organisms and corresponding objects stored in the database are organized in taxonomic groups to facilitate the recognition in multi organism samples and to enable a specific design for the analysis where e.g. plants differ in recorded measurements from mammals. The taxonomic groups are roughly orientated on the taxonomy but are not meant to replace the taxonomy for which there are other possibilities for entry. The list of taxonomic groups visible for the creation of new entries may be restricted as described in the chapter about the customization.
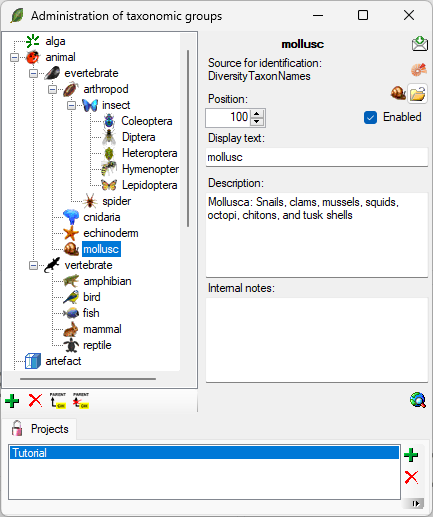
To administrate the taxonomic groups, choose Administration - Taxonomic groups... from the menu. A window as shown below will open.

To add resp. remove a taxonomic group use the
 resp.
resp.
 button. To set the superior taxonomic
group use the
button. To set the superior taxonomic
group use the
 button. With the
button. With the
 button you can
set a symbol for the taxonomic group. Please keep in mind, that
this will be converted into a 16 x 16 size icon. In the lower
part of the window, you can add and edit translations for
display texts, abbreviations etc. for all contexts available.
button you can
set a symbol for the taxonomic group. Please keep in mind, that
this will be converted into a 16 x 16 size icon. In the lower
part of the window, you can add and edit translations for
display texts, abbreviations etc. for all contexts available.
At the base of the window, the
projects that are restricted to an entry are listed (see
 ).
To
administrate the projects that should restrict the available taxonomic groups, choose Administration -
Enumerations - Project - Taxonomic group...
from the menu. A window as shown below will open. If a
project is restricted, the client settings will be ignored (see
chapter Customize).
).
To
administrate the projects that should restrict the available taxonomic groups, choose Administration -
Enumerations - Project - Taxonomic group...
from the menu. A window as shown below will open. If a
project is restricted, the client settings will be ignored (see
chapter Customize).
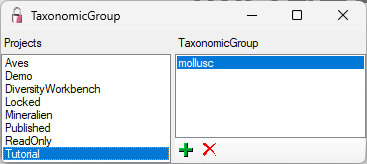
To add resp. remove a material category
for a project use the  resp.
resp.
 button.
button.
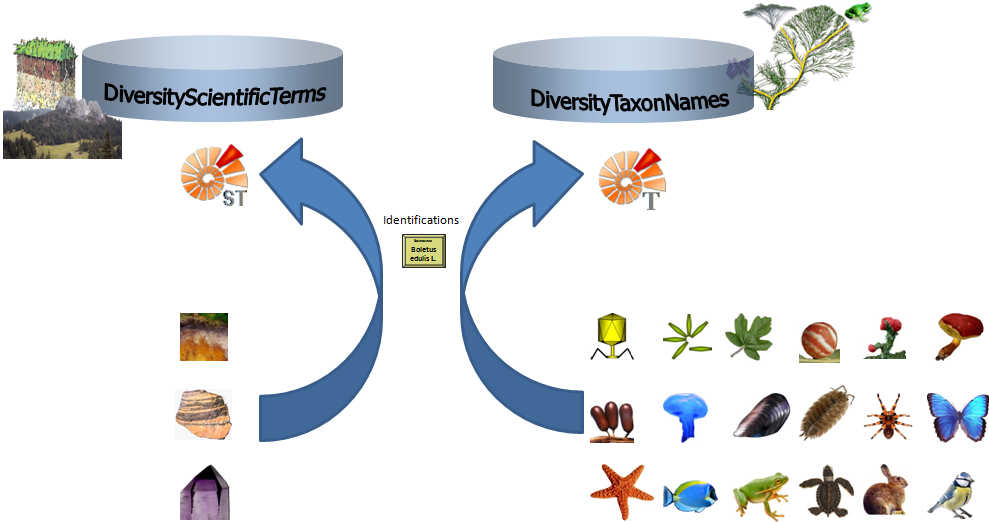
The
non-biological taxonomic groups like
 soil,
soil,
 rock or
rock or
 mineral will for an identification not be linked to
DiversityTaxonNames but to DiversityScientificTerms (see image below and the
short tutorial
mineral will for an identification not be linked to
DiversityTaxonNames but to DiversityScientificTerms (see image below and the
short tutorial 
 ). If you add a new taxonomic
group anything outside the predefined groups animal, alga, bacterium, bryophyte,
fungus, gall, lichen, myxomycete, plant or virus will be regarded as
non-biological. The sources for direct access using the
). If you add a new taxonomic
group anything outside the predefined groups animal, alga, bacterium, bryophyte,
fungus, gall, lichen, myxomycete, plant or virus will be regarded as
non-biological. The sources for direct access using the
 buttons are linked to the taxonomic groups (see Settings).
buttons are linked to the taxonomic groups (see Settings).