Translations
Translations
For each project a default language is selected in the Edit
project panel. In Diversity Descriptions for most
database entries additionally translated expressions can be stored in
the Translation table. Even for
the default language adjusted for the project alternate expressions may
be entered. In several export and document generation forms it is
possible to select an alternate output language, if translations are
available. Translatable entities are listed in the following table.
|
|
| Database table |
Database columns |
| CategoricalState |
label, detail, abbreviation, wording |
| DataStatus_Enum |
label, detail, abbreviation |
| Description |
label, detail, wording |
| Descriptor |
label, detail, abbreviation, wording_before, wording_after, wording |
| DescriptorTree |
label |
| DescriptorTreeNode |
label, detail, abbreviation |
| Frequency |
label |
| Modifier |
label |
| OtherScope |
label, detail |
| Project |
label, detail |
| Resource |
label, detail |
| ResourceVariant_Enum |
label, detail |
| SamplingEvent |
label, detail |
| SexStatus_Enum |
label, detail, abbreviation |
| StatisticalMeasure_Enum |
label, abbreviation |
All mentioned entities may be edited using the translationseditor. If for an output a translation language
is specified, a situation may occur that for a certain entity not
translation is stored in the database. In those cases automatically the
original database values will be used.
As you can see in the table above, no translations are supported for the
descriptive data, i.e. summary or sampling data. Concerning categorical
data, there is a tranlsation support, because the terminology parts
(Descriptor and CategoricalState) my be translated. Quatitative data
mainly include numeric values and their statistical measure, where the
measure texts themselves can be translated. The same is valid for
descriptor status data. Molecular sequence data naturally do not contain
any translatable texts. Finally only the contents of text descriptor
data and notes, that can be included in any summary or sampling data,
are not supported for translation.
Data export
The export format SDD is XML based and offers multilingual support.
By default the document language ist set to the project default language
and the original database entries (labels, detail texts and so on) are
included without explicit language tag. If translations are stored in
the database, they are included in the SDD output with their specific
language tag. As an option translations may be completely excluded from
export or the SDD document language may even be switched to one of the
available translation languages. Please be aware, that the enumerated
values (DataStatus_Enum, StatisticalMeasures_Enum and SexStatus_Enum)
are identified by specific tags within SDD. Therefore the translations
for these are not included in the SDD file!
The export format DELTA is text based and does not support
multilinguality. By default the original database entries are used in
the DELTA output. If translations are stored in the database, you may
select one of the available languages for the DELTA output.
In both cases the general rule applies that if for a certain term no
translated value is present, the original value will be used. For
details concerning the data export see here.
Data import
In the SDD import form the available languages are
displayed. You have the options to omit translations during import or
select a different language as the project’s default language.
The DELTA import form offers the option to import
translations for descriptors, categorical states and description items
from separate DELTA files with identical structure. In a first step the
complete data are imported form a main DELTA file. In subsequent steps
the identifier for additional languages may be imported from additional
language specific DELTA files.
Document generators
The is a number of document generators to
generate HTML or Media Wiki output. In this form an “Export language”
field is shown if any translations are available in the database. In
those cases you have the choice to adjust the default language or one of
the offered tranlsations languages. Anyway, there may be some fixed
expressions in the generated documents, where currently no mutilingual
support is available.
Subsections of Translations
Edit Language Codes
Edit language codes
In the Diversity Descriptions database language codes are used for two
purposes: The first one is to indicate the project’s default language.
Furthermore for the most important parts of the data
translations may be entered, which carry a laguage
code, too.
By all means the language codes consists of an at most three-letter
string. In the application you may select the language code from a
drop-down box, which shows the language code - in most cases a
two-letter ISO 639-1 code - and the corresponding long name. By clicking
the  button you may change the display sequence (see
images below).
button you may change the display sequence (see
images below).
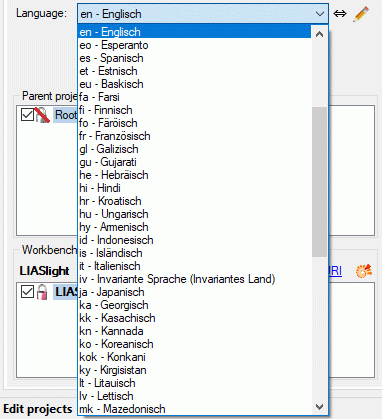

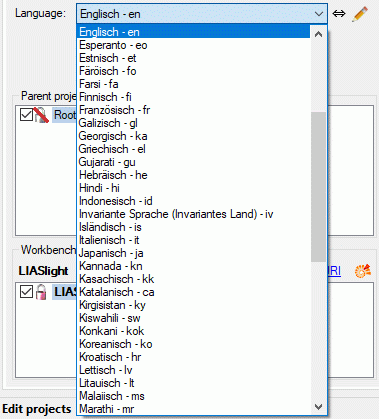
Most of the values are provided by the operating system. Anyway there
might be the need to include additional values, e.g. “eo” for Esperanto.
For those cases as a second source additional language codes may be
stored in the application’s settings. Finally, language codes that are
present in the database but neither included in the operating system’s
list nor the application settings will be included at the end of the
selection list with red background, if
neccessary.
To edit the language codes, click the  edit button and
a new window will open (see image below). The operating system’s entries
are shown with a light blue background and
cannot be modified. The language codes that are stored in the
application settings are shown with white background and may be edited.
To enter a new value, use the empty line at the end of the table. To
delete an entry, mark the whole line by clicking on the row header and
press the delete key on the keyboard.
edit button and
a new window will open (see image below). The operating system’s entries
are shown with a light blue background and
cannot be modified. The language codes that are stored in the
application settings are shown with white background and may be edited.
To enter a new value, use the empty line at the end of the table. To
delete an entry, mark the whole line by clicking on the row header and
press the delete key on the keyboard.
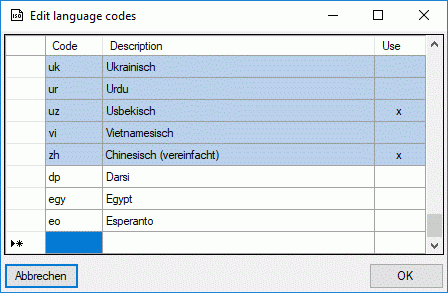
By clicking OK the changes will be
stored in the settings.
Edit Translations
Editing translations
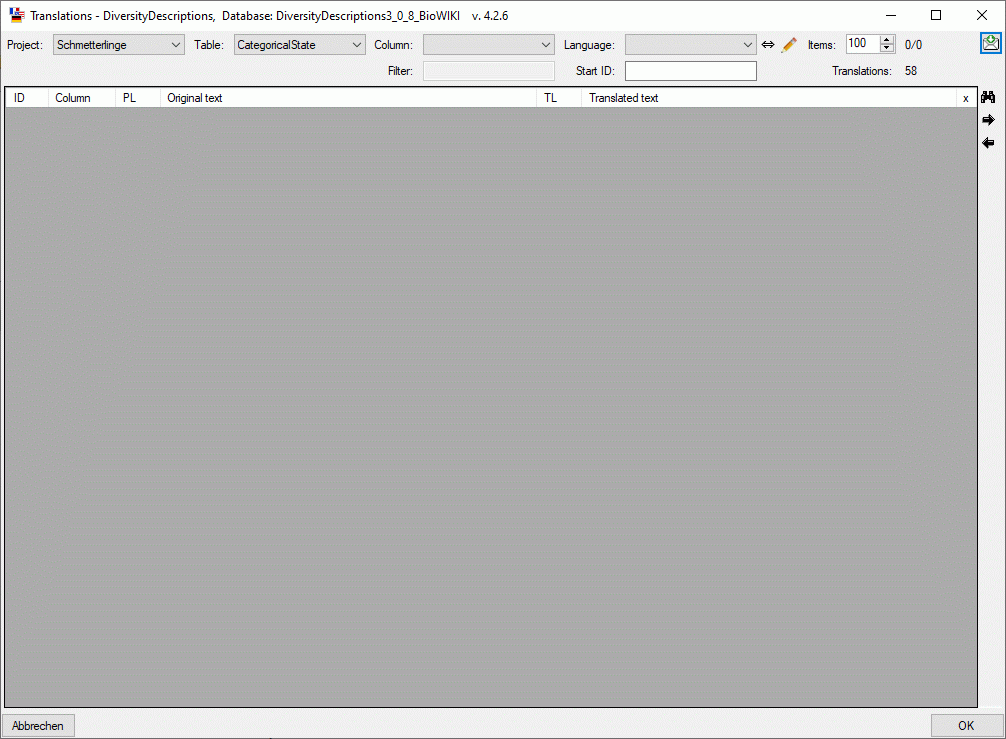
After connecting a database select Edit ->
 Translations … from the menu (see image
below). You have to select the mandatory parameter Project and the
Table. If you want to enter a new translation text, the Column
and the target Language must be selected. If you omit one of those
parameters, only existing tranlation texts from the database will be
shown. Anyway the number of translations that match the currently
selected criteria will be shown in field Translations in the upper
right area of the form.
Translations … from the menu (see image
below). You have to select the mandatory parameter Project and the
Table. If you want to enter a new translation text, the Column
and the target Language must be selected. If you omit one of those
parameters, only existing tranlation texts from the database will be
shown. Anyway the number of translations that match the currently
selected criteria will be shown in field Translations in the upper
right area of the form.
You man change the display and sorting of the entries in the
Language combo box from “<code> - <description>” to
“<description> - <code>” (and back) by clicking the button
 . If you need language codes that are not included
in the list, click the
. If you need language codes that are not included
in the list, click the  edit button. For more details
see Edit language codes.
edit button. For more details
see Edit language codes.
With the numeric control Items you may adjust how many database
items shall be selected for display. After clicking the
 button the query results are displayed. By
clicking the buttons
button the query results are displayed. By
clicking the buttons  and
and
 you can load the next rsp. previous
matches.
you can load the next rsp. previous
matches.
When you select a Column, an additional text box Filter is
activated, where you may restrict the displayed datasets to matching
entries in the Original text (see image below). In field Start
ID the first ID of the current output is shown. You may enter a
dedicated value to be used for the next output.
The table lists the internal ID of the data entry (“ID”), the table
column (“Column”), the project language (“PL”), the “Original text”, the
translation language (“TL”) and the “Translated text” (see image
below). In table column “x” lines without write access will be marked as
x . If you have write access, you may enter
the tranlated text directly in the table.
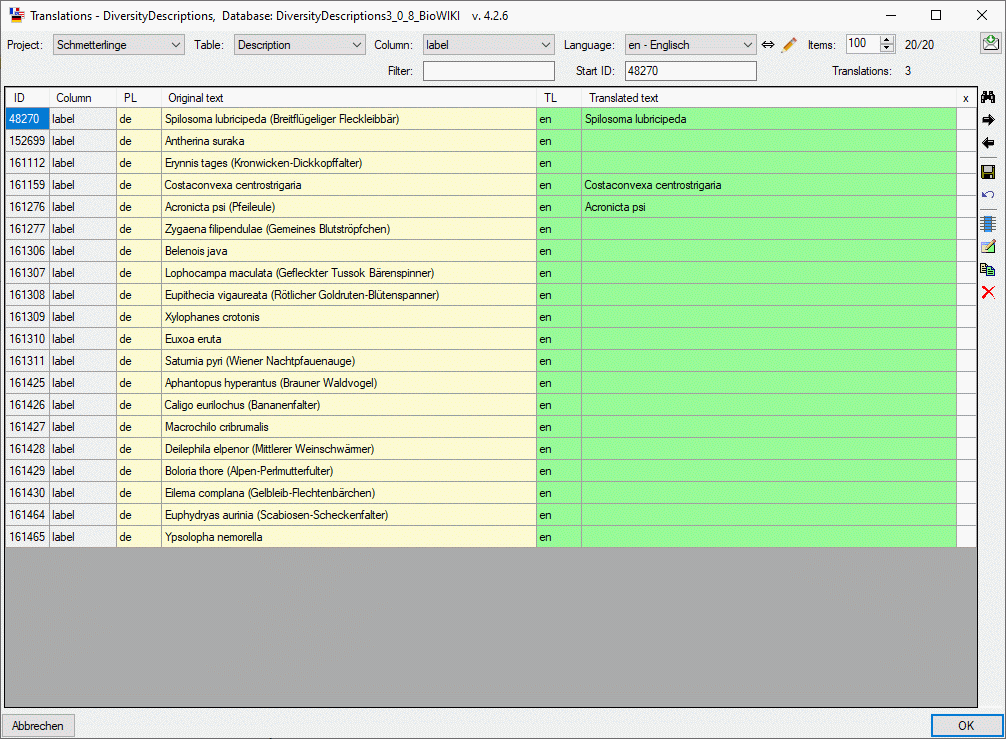
You may copy the original text of selected lines to the translated text
by clicking the button  or delete the
translated text with button
or delete the
translated text with button  . To select all
translated texts click on button
. To select all
translated texts click on button  . In modified
lines the background color of the first two columns will be change to
yellow (see image below). With button
. In modified
lines the background color of the first two columns will be change to
yellow (see image below). With button
 you can save the modified data, with button
you can save the modified data, with button
 you can reload the table, i.e. discard the
changes.
you can reload the table, i.e. discard the
changes.
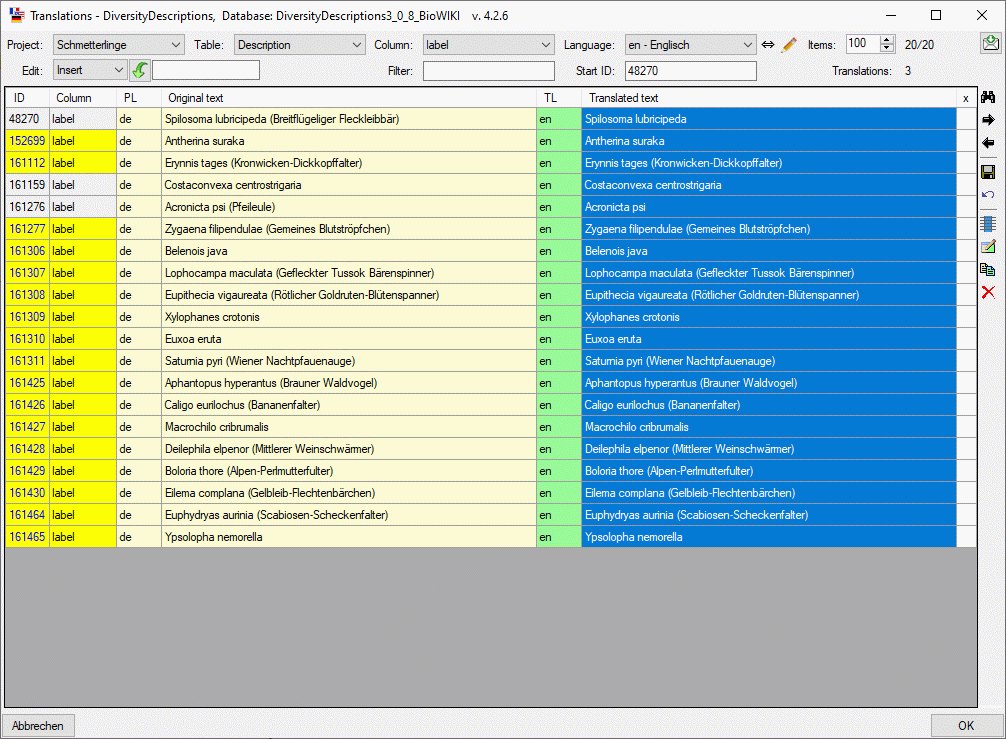
If you selected any Translated text entries, it is possible to
modify several values simultaneously. Therefore select the table entries
that shall be edited - by clicking the button  you may select the whole table column. Then select the required
operation in the Edit section: “Insert”, “Append” or “Replace” and
enter the new rsp. new and old value. After clicking the action button -
depending on the selected operation this is
you may select the whole table column. Then select the required
operation in the Edit section: “Insert”, “Append” or “Replace” and
enter the new rsp. new and old value. After clicking the action button -
depending on the selected operation this is  (Insert),
(Insert),  (Append) or
(Append) or  (Replace).
(Replace).
By double-clicking the table line or clicking the
 button you can open a separate
edit window (see image below). This form works almost in the same way as
the Extended text editor.
button you can open a separate
edit window (see image below). This form works almost in the same way as
the Extended text editor.


 button you may change the display sequence (see
images below).
button you may change the display sequence (see
images below). 




 Translations … from the menu (see image
below). You have to select the mandatory parameter Project and the
Table. If you want to enter a new translation text, the Column
and the target Language must be selected. If you omit one of those
parameters, only existing tranlation texts from the database will be
shown. Anyway the number of translations that match the currently
selected criteria will be shown in field Translations in the upper
right area of the form.
Translations … from the menu (see image
below). You have to select the mandatory parameter Project and the
Table. If you want to enter a new translation text, the Column
and the target Language must be selected. If you omit one of those
parameters, only existing tranlation texts from the database will be
shown. Anyway the number of translations that match the currently
selected criteria will be shown in field Translations in the upper
right area of the form.
 button the query results are displayed. By
clicking the buttons
button the query results are displayed. By
clicking the buttons  and
and
 you can load the next rsp. previous
matches.
you can load the next rsp. previous
matches. 
 or delete the
translated text with button
or delete the
translated text with button  . To select all
translated texts click on button
. To select all
translated texts click on button  . In modified
lines the background color of the first two columns will be change to
. In modified
lines the background color of the first two columns will be change to
 you can save the modified data, with button
you can save the modified data, with button
 you can reload the table, i.e. discard the
changes.
you can reload the table, i.e. discard the
changes. 
 (Insert),
(Insert),  (Append) or
(Append) or  (Replace).
(Replace).