Diversity Taxon Names
Export
There are several options to export data.
- Export of hierarchy and synonymy
- Export of taxon list information
- Export via list view
- Export via export wizard
There are several options to export data.
To export the tables of the database in a tabulator, comma or semicolon separated format, choose Data → Export → Export CSV... from the menu. A window as shown below will open where you can select the tables to be exported in sections Selection criteria and in the Tables for export.
A prerequisite for this export is that the bcp program is installed on your computer. This has either been installed together with the installation of SQL-Server or you have to install the Microsoft Command Line Utilities for SQL Server.
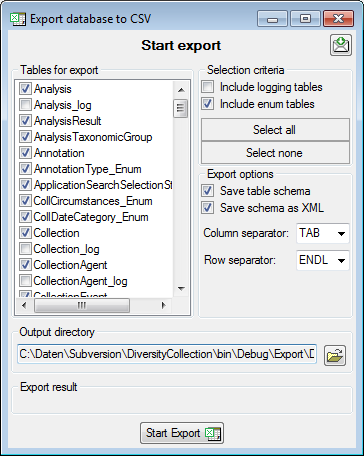
To start the export click on the Start export 

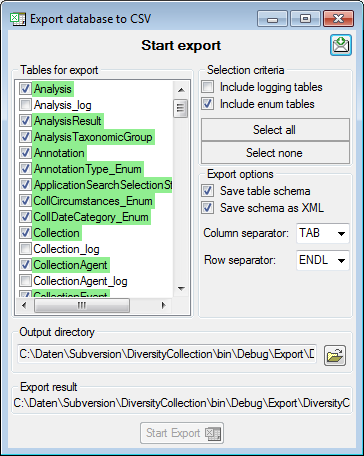
After export the tables are marked with green background, if table schema and data were exported successfully. If only the data were exported, this is marked with yellow background, if nothing was exported, the background is red. A detailed export report can be viewed by a click on the export result file name.



 One parallel table
One parallel table Several parallel tables according to
selected data
Several parallel tables according to
selected data Dependent table
Dependent tableAll options will include the depending tables as defined for the default
table. The 
If you added parallel tables, you should set the sequence of the
datasets within these tables: For the columns that should be used for
sorting the data, set the ordering sequence to a value > 0 and choose
if the ordering sequence should be ascending 

 Certain columns in the database may provide information linked to
another table
Certain columns in the database may provide information linked to
another table 

 button
to add a linked value.
button
to add a linked value.




 on the left side of the column that will change to
on the left side of the column that will change to  for fused columns. To remove a file column, use the
for fused columns. To remove a file column, use the 




 This filter in contrast to the filter above strictly applies to the row
according to the sequence of the data. For an explanation see a short
tutorial
This filter in contrast to the filter above strictly applies to the row
according to the sequence of the data. For an explanation see a short
tutorial





If you want to inspect the SQL commands created during the test check this option. To see the generated SQL click on the SQL button after the Test export. A window containing all commands including their corresponding tables will be shown.






 To export your data into a SQLite
database, choose the
To export your data into a SQLite
database, choose the  Export to SQLite tab. You may change the preset name of the database in order to keep previous exports. Otherwise you overwrite previous exports with the same filename. To start the export, click on the Export data
Export to SQLite tab. You may change the preset name of the database in order to keep previous exports. Otherwise you overwrite previous exports with the same filename. To start the export, click on the Export data
 button. To view the exported data, use the
button. To view the exported data, use the










Here you can enter 6 types of transformation that should be applied to
your data. 




With the cut transformation 


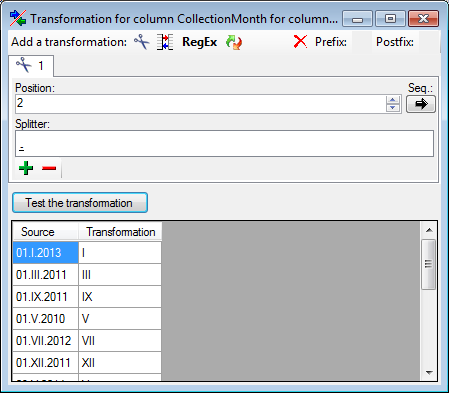
With the Start at Pos. option the given splitters will be converted into space (' ') and the whole string starting with the given position will be used (see below).
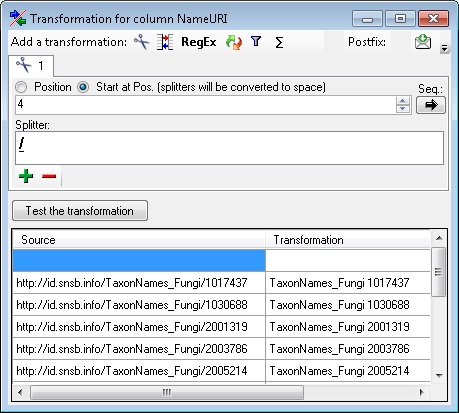
The translate transformation 






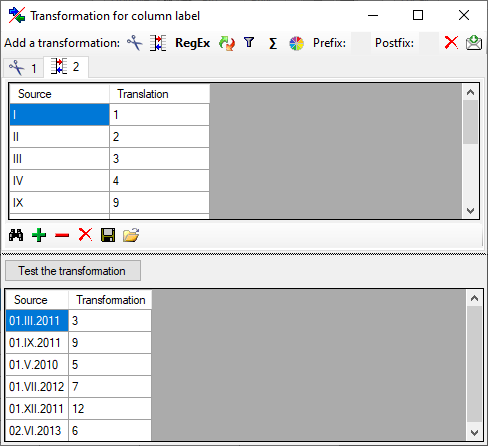
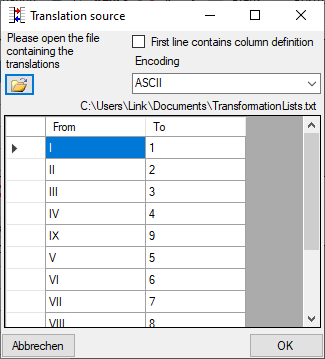
To load a predefined list for the transformation use the


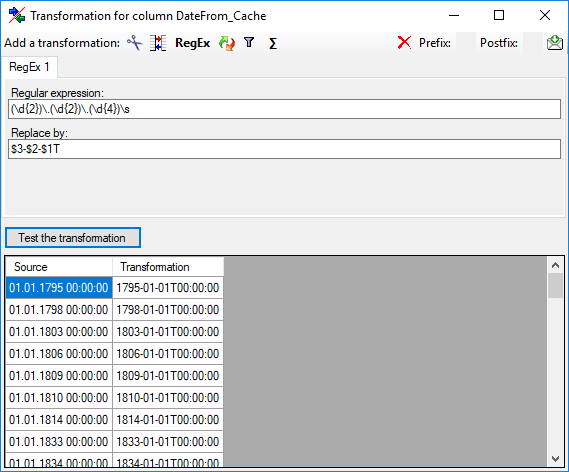
The transformation RegEx using regular expressions will transform the values according to the entered Regular expression and Replace by values. For more details please see documentations about regular expressions.
The replacement transformation 
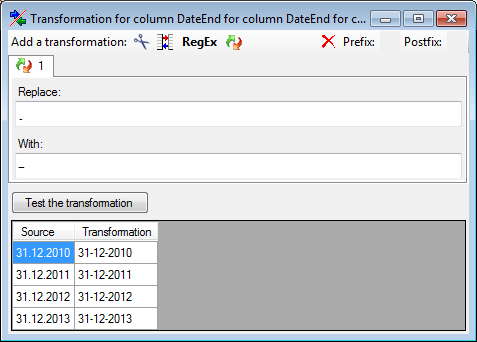
The calculation transformation Σ performs a calculation on numeric value, dependent on an optional condition. In the example below, 2 calculations were applied to convert 2-digit values into 4 digit years.
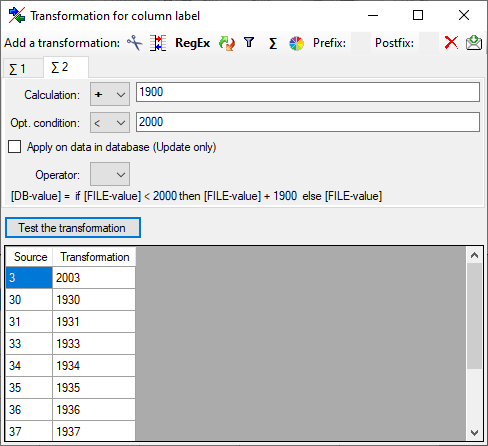
The filter transformation 





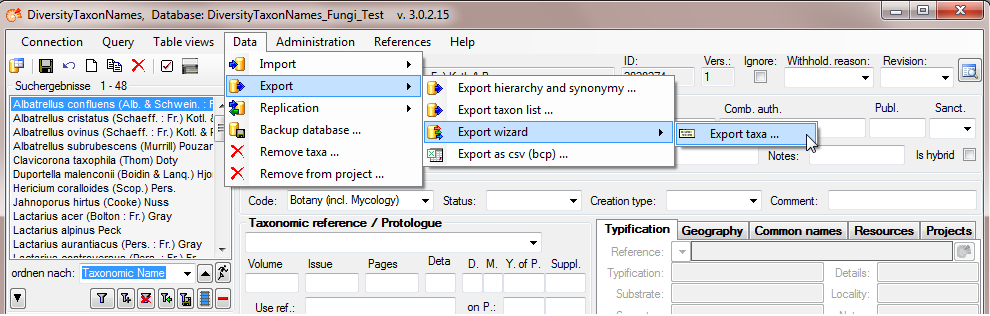
This tutorial demonstrates the export of a small sample of data from the database.
In the main form, select the data that should be exported (only the data displayed in the query results are exported).
Choose Data → Export → 

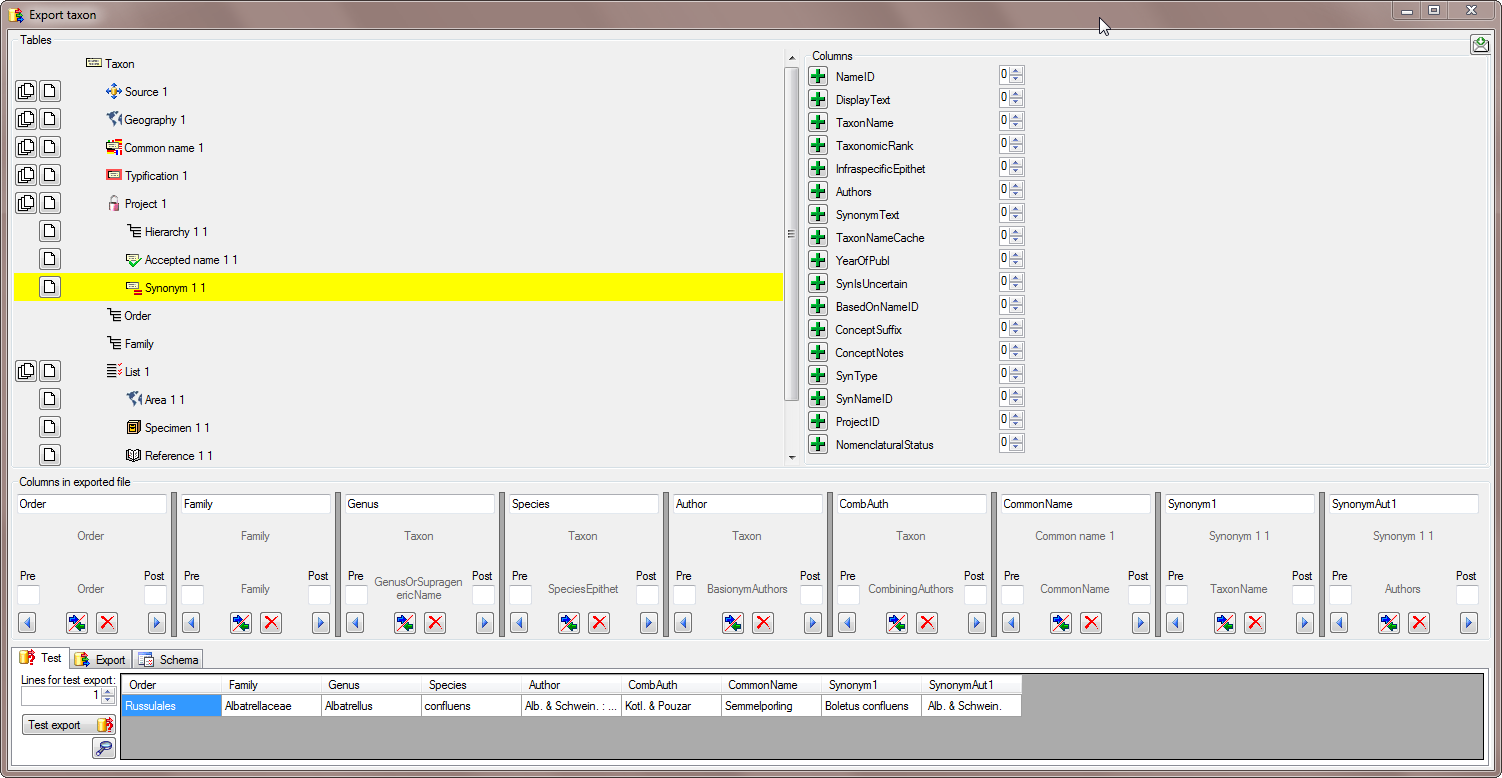
A window as shown below will open where the available tables for export are listed in the upper left area. To show the data colums of a table, select this table in the list.
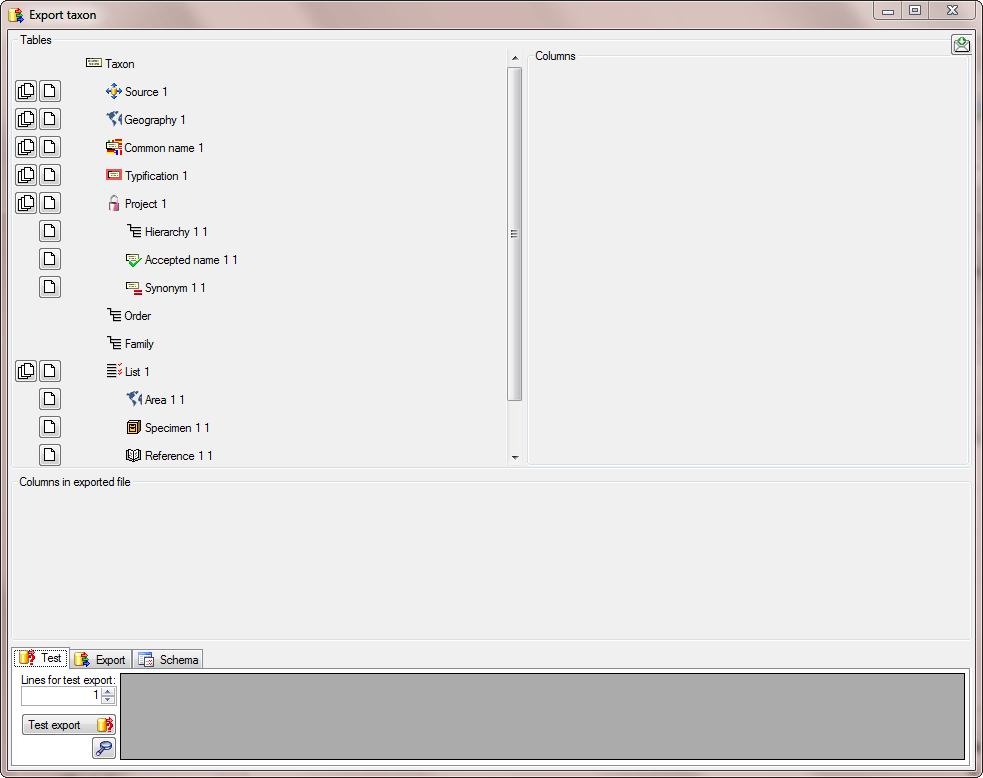
In this example, we want to add the higher hierarchy, starting with the
order. Select the Order from the list as shown
below.
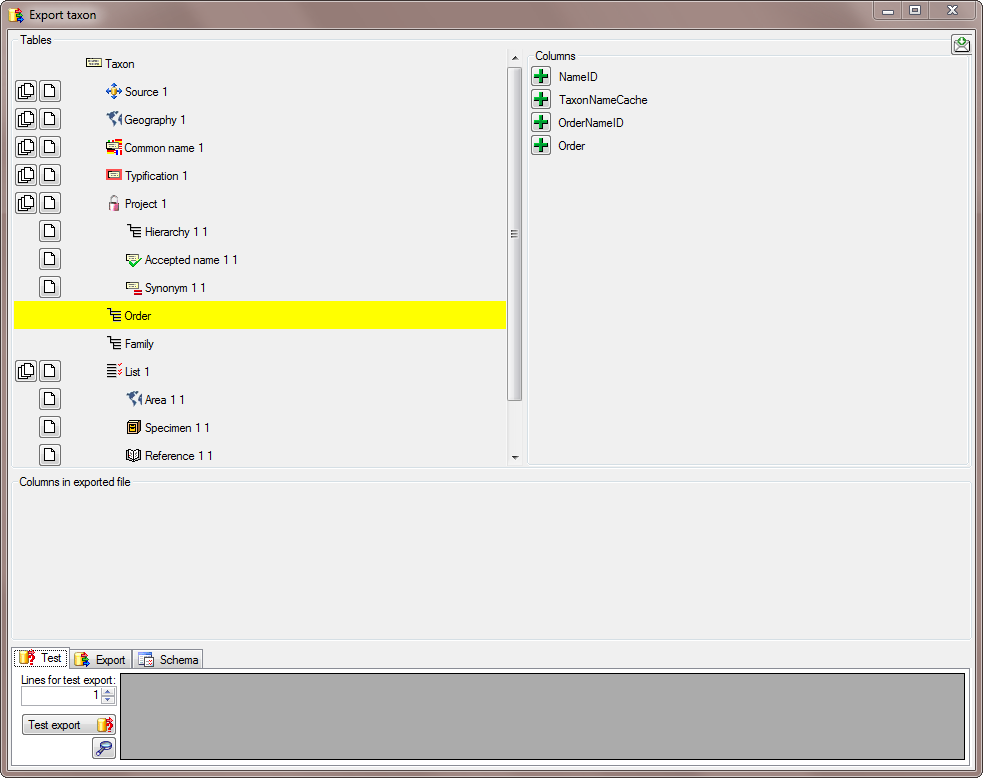
In the Columns area appearing in the area on the right click on the

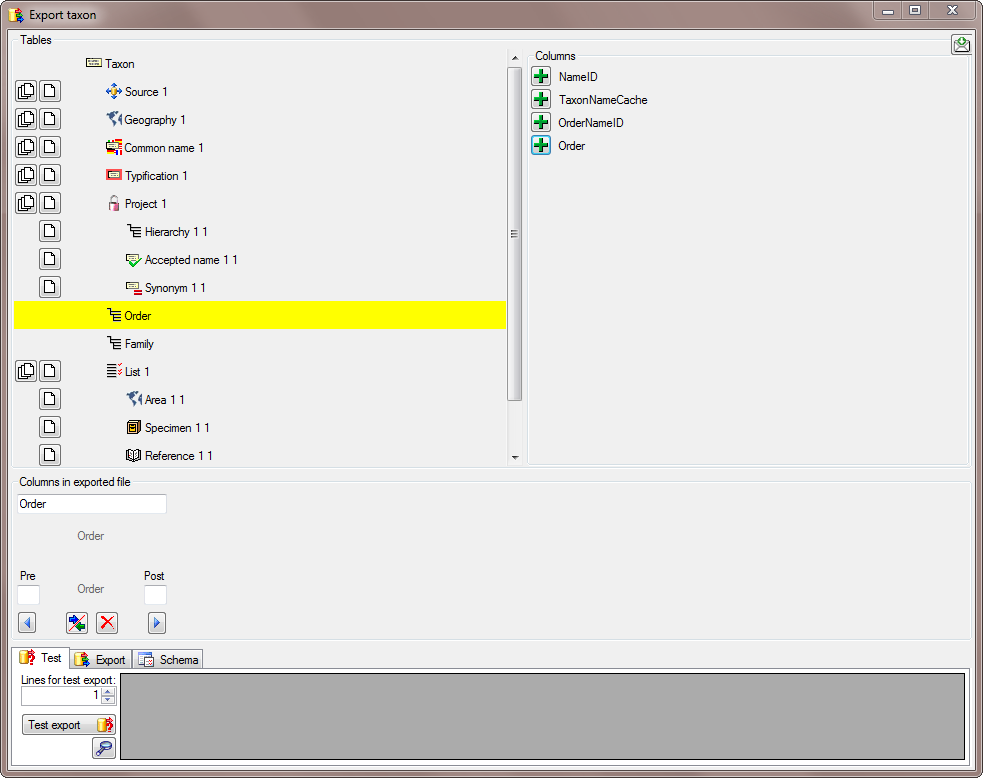
This is repeated for the Family and the Genus
(see below).
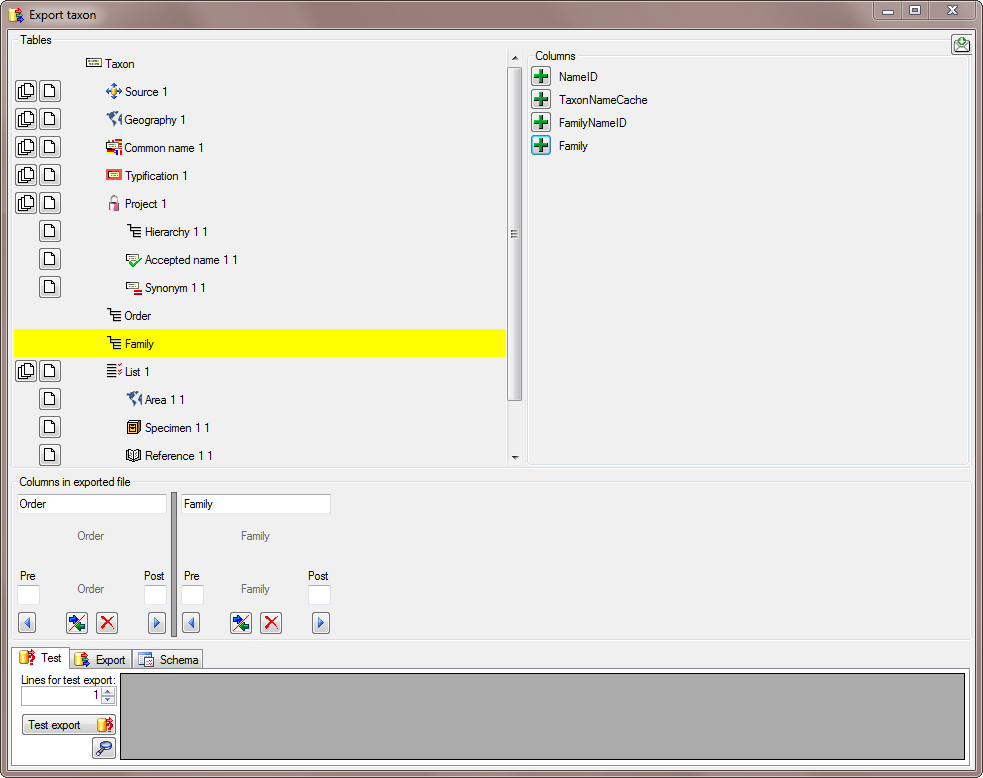
In the taxon table choose the column GenusOrSupragenericName to add teh genus to te exported (see below).
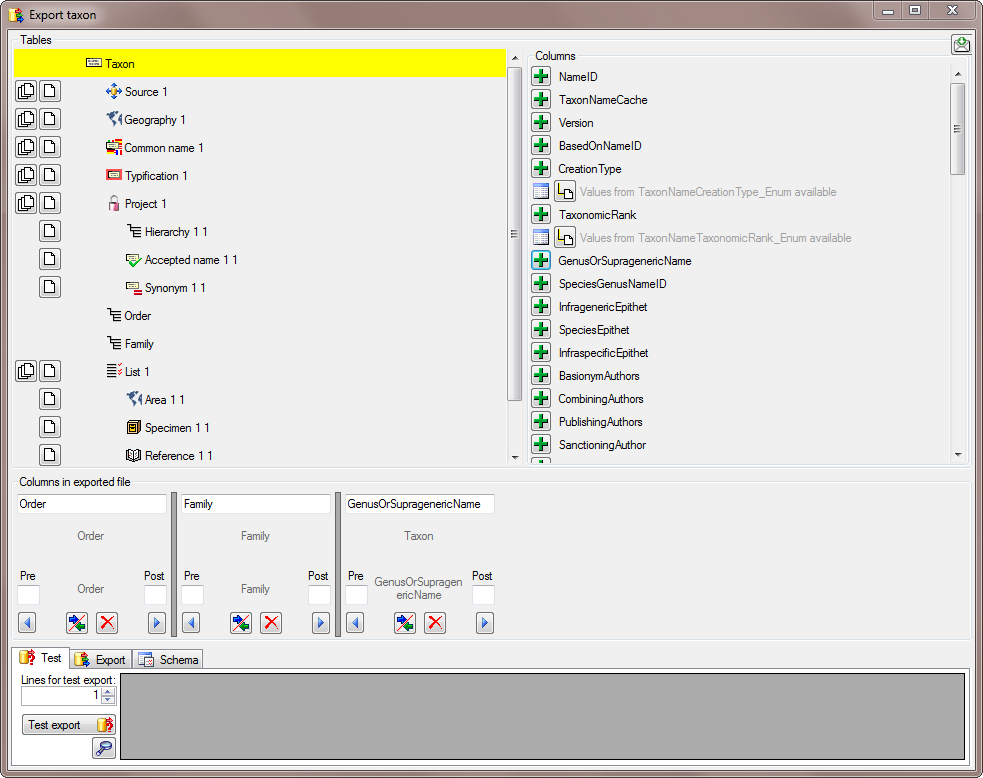
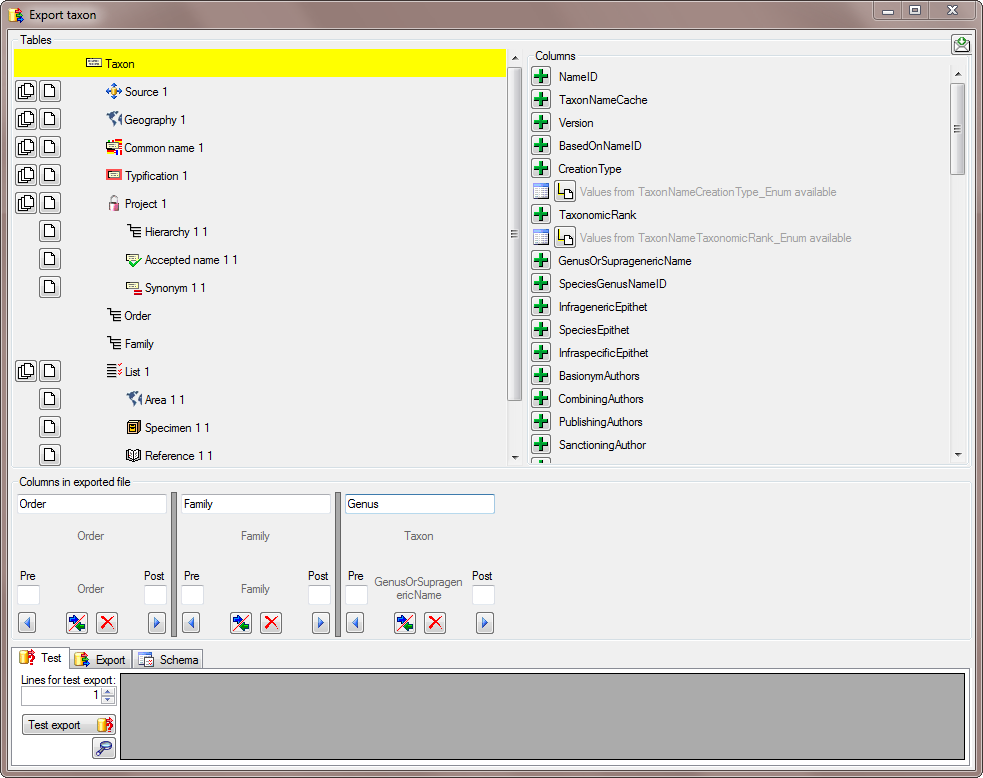
To avoid that the column name GenusOrSupragenericName appears in our export, we change the name to Genus (see below).
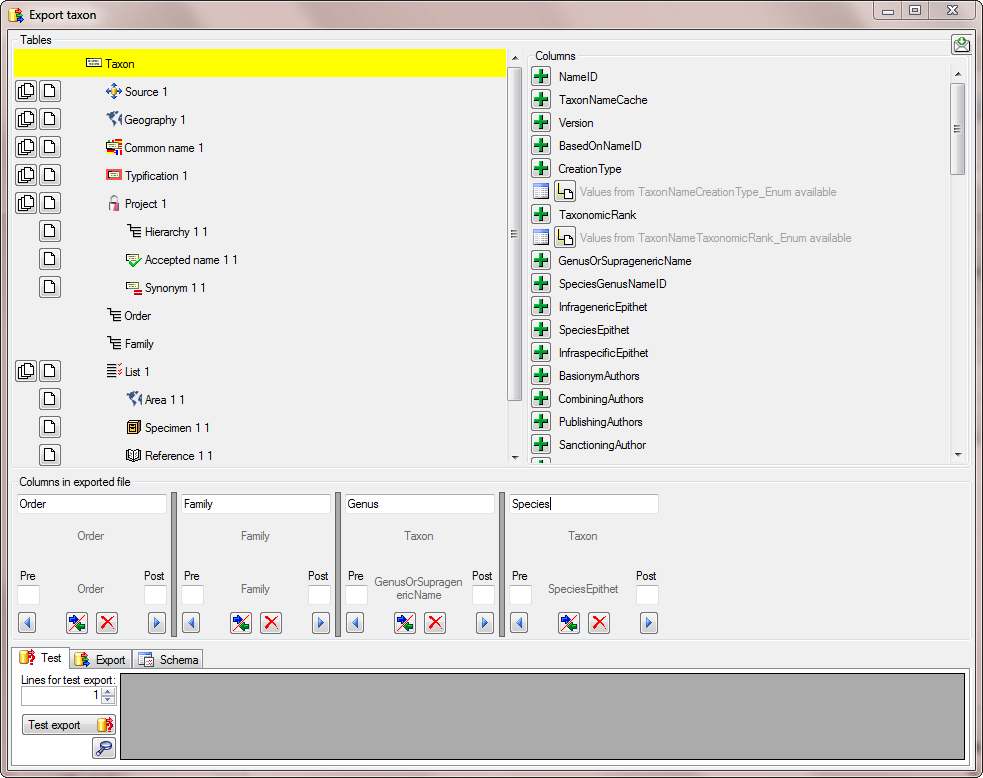
The same is repeated for the species, authors, common names and synonyms (see below).
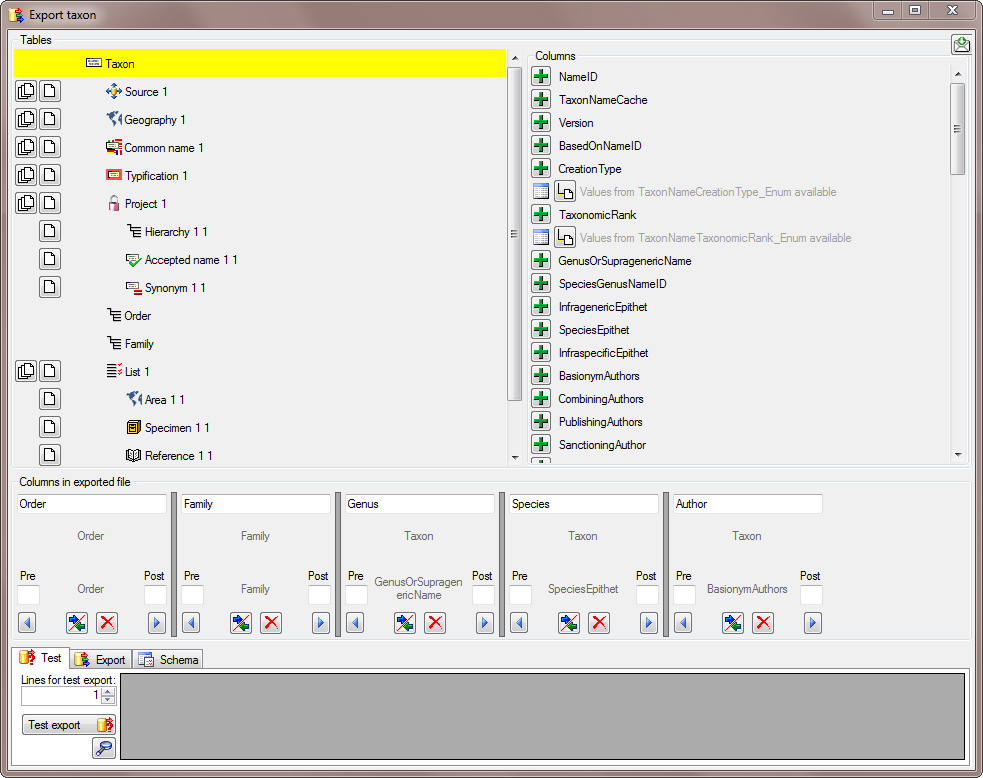
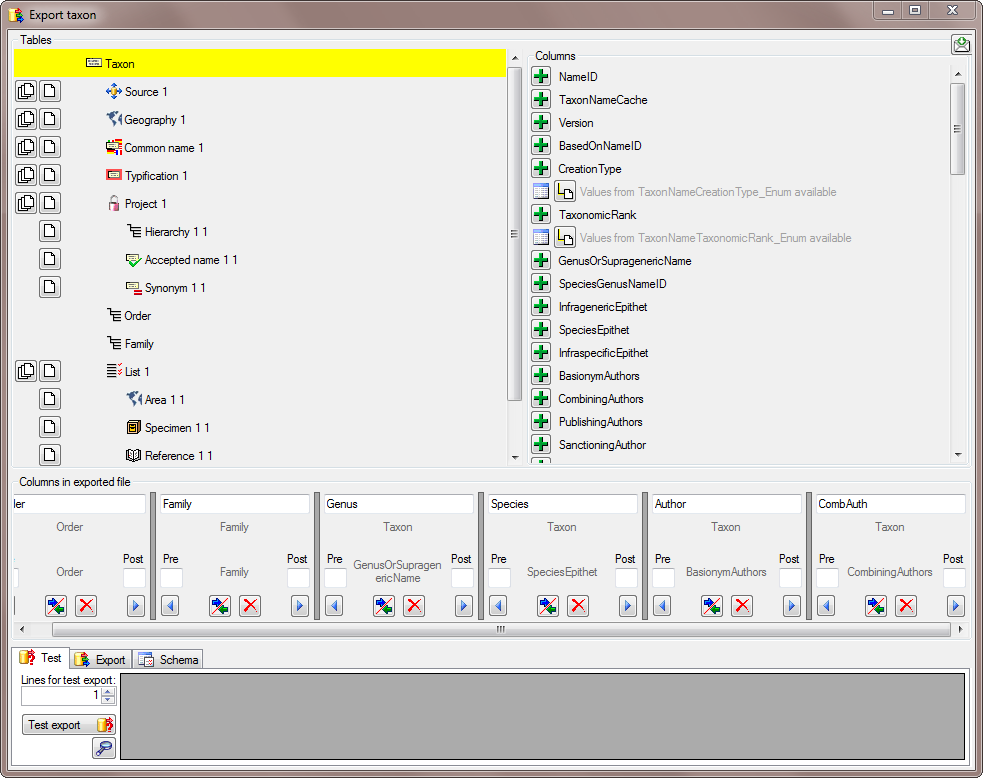
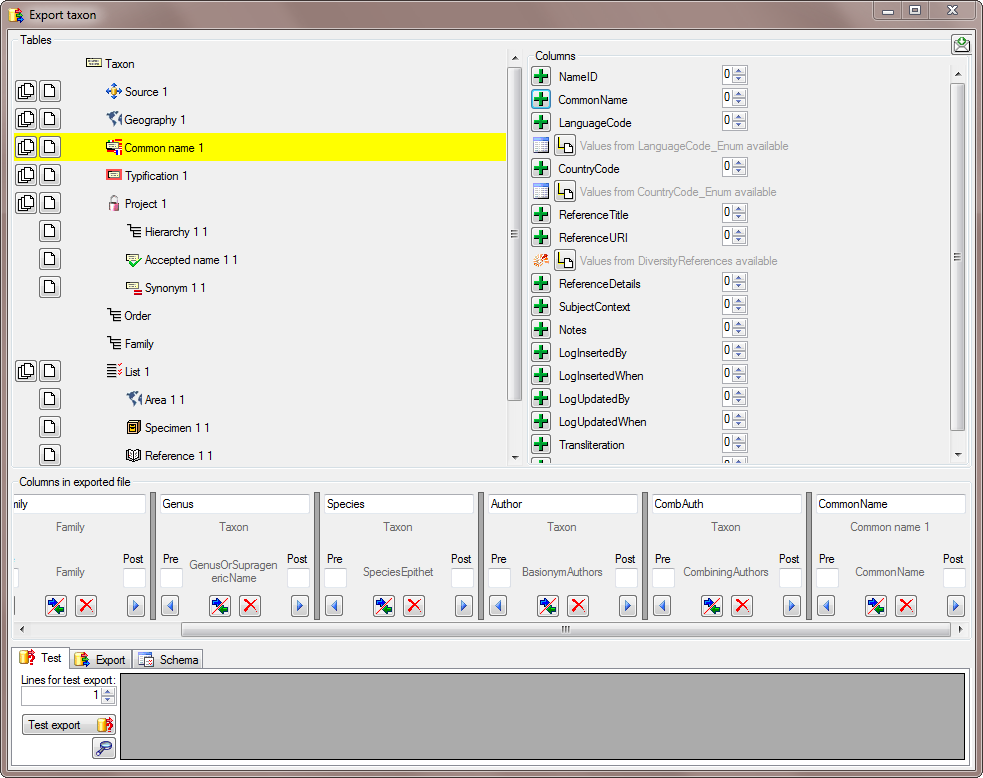
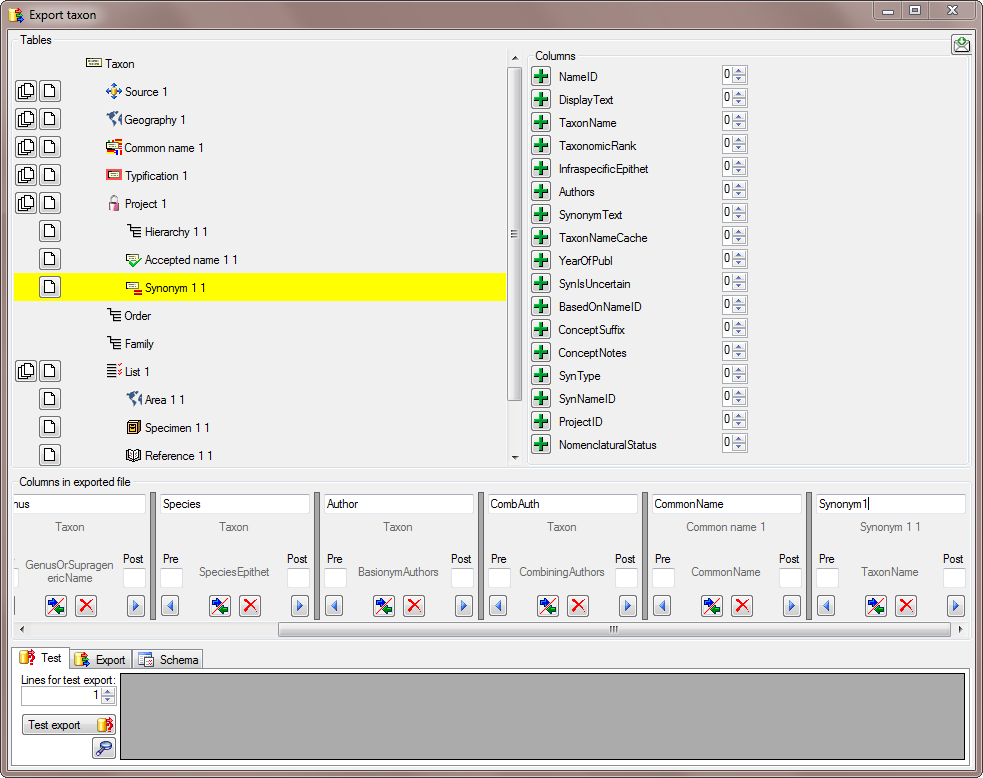
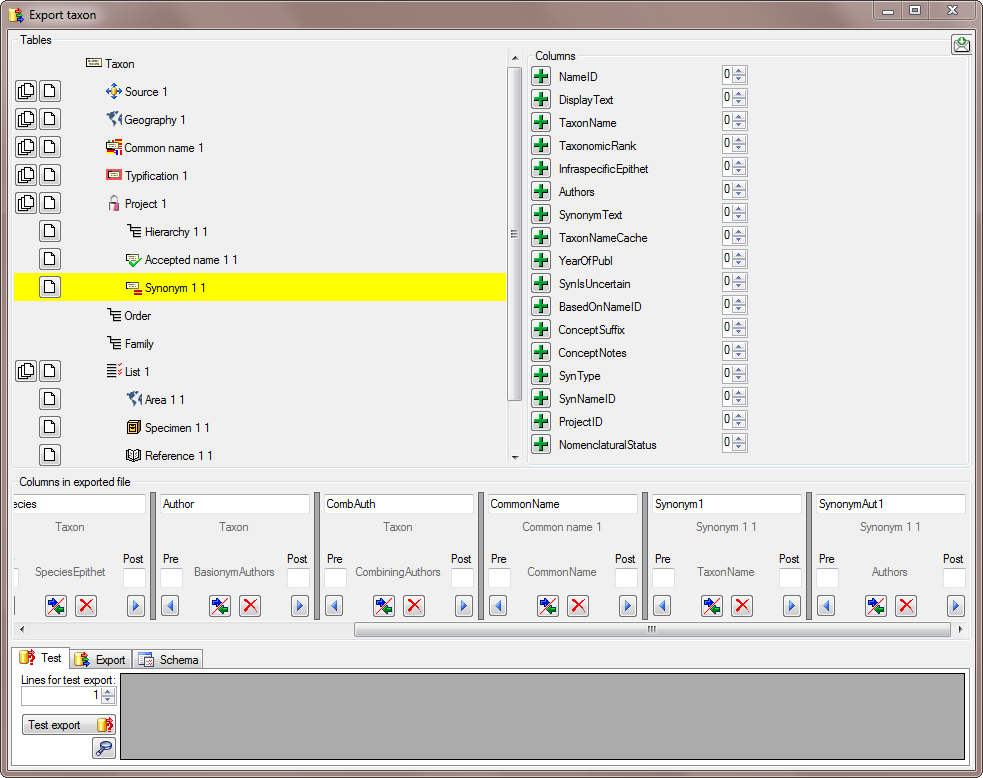
After all columns that should be exported and their transformations are
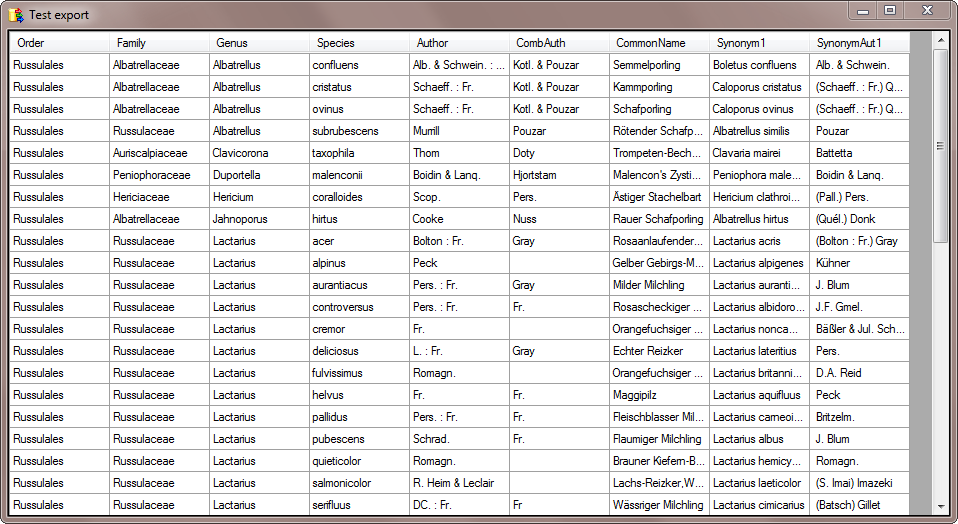
defined, we start Test export 
Click on the 
To export the data change to the 

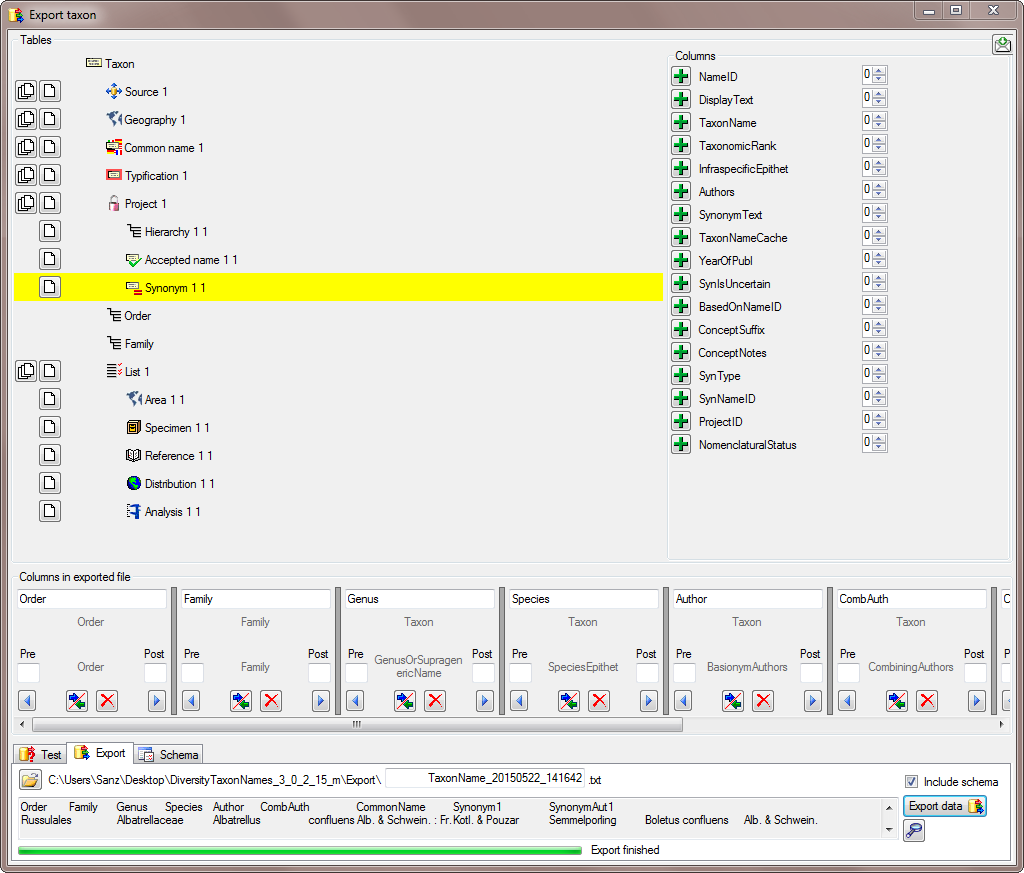
Together with the exported data, a schema is stored, containing all settings of the export. This schema may be reused for subsequent exports of the same type (see below).

To export the taxonomy, including the hierarchy and the synonymy, select the corresponding taxon, choose Data → Export → Export hierarchy and synonymy… from the menu.
To see the whole
hierarchy, select the desired node in the hierarchy tree and click on
the 
A window as shown below will open
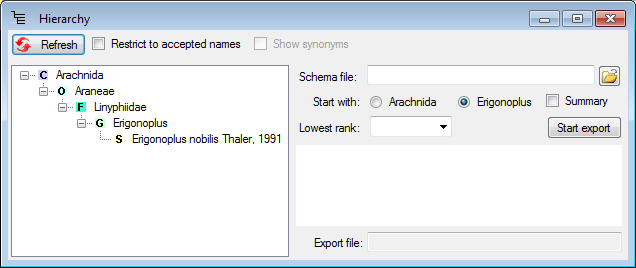
The data you in the export will depend upon the taxon you selected in the main form. So if e.g. you want to export the names within a genus, select the genus in the main form.
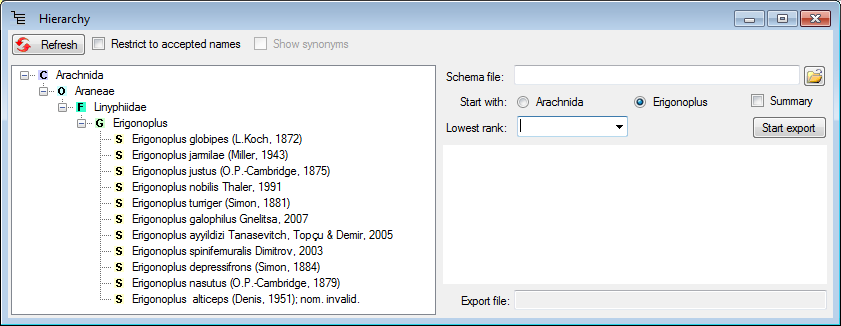
If you want to
include the synonyms, check Restrict to accepted names and Show
synonyms and click on the 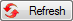 button (see
below).
button (see
below).
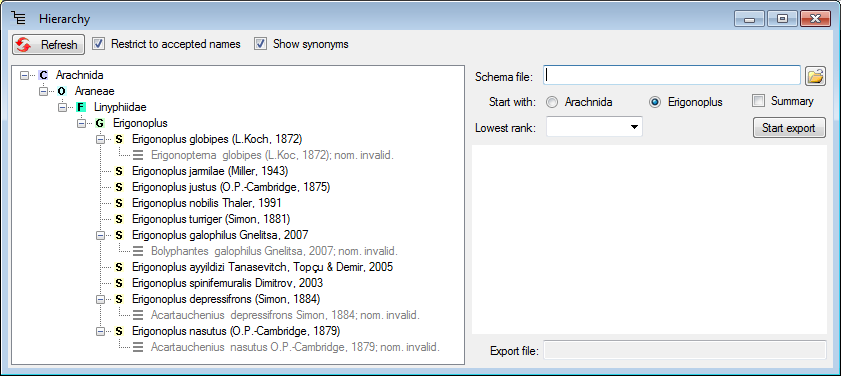
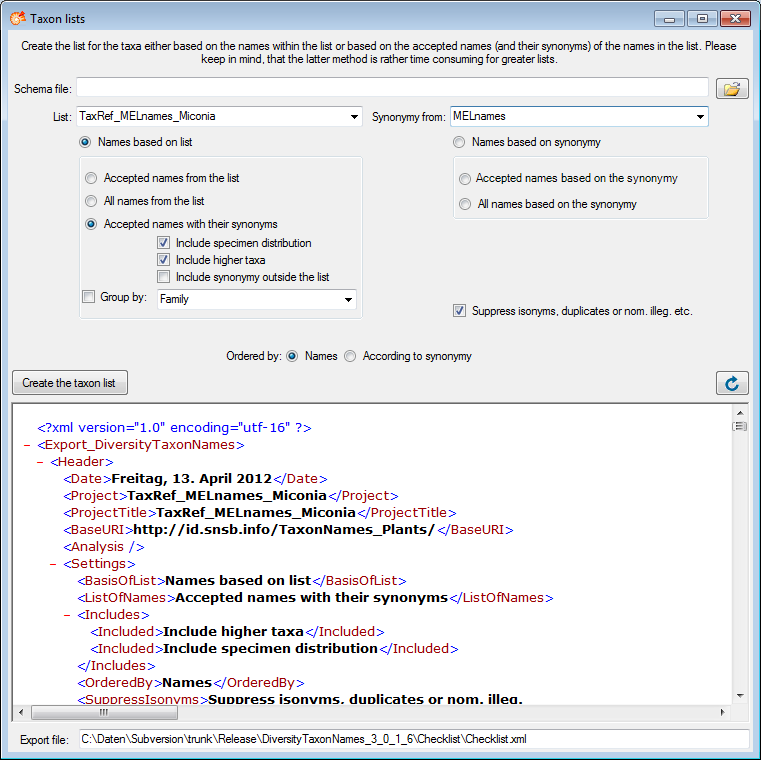
If you start the export without any schema file, you will get the data strutured as xml (see below).
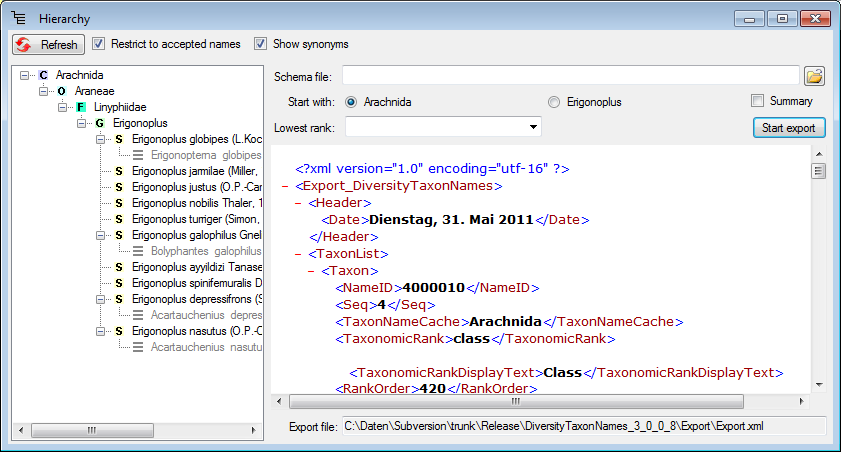
To format the data, specify the schema file containing your preferred format as shown below.
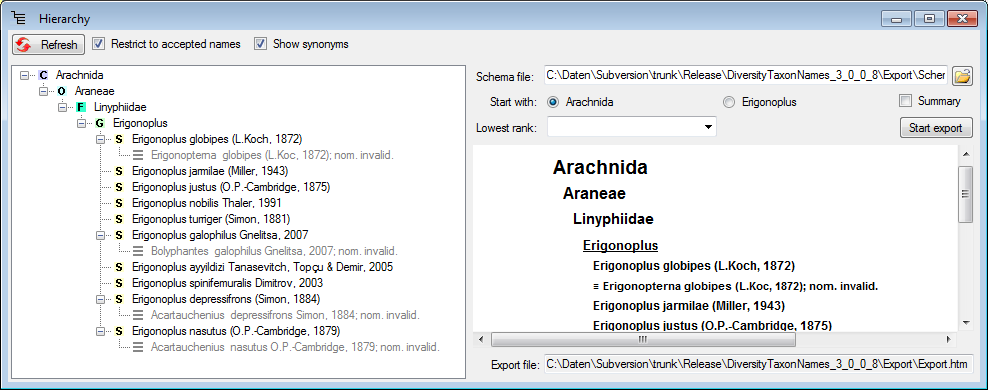
You can export the data including all higher taxa (see above) or starting with the taxon for which you selected the export (see below). mao format the data, specify the schema file containing your preferred format as shown below.
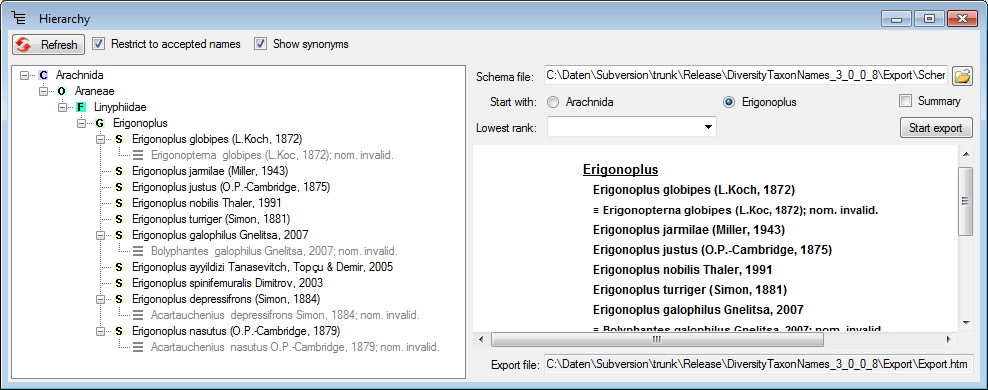
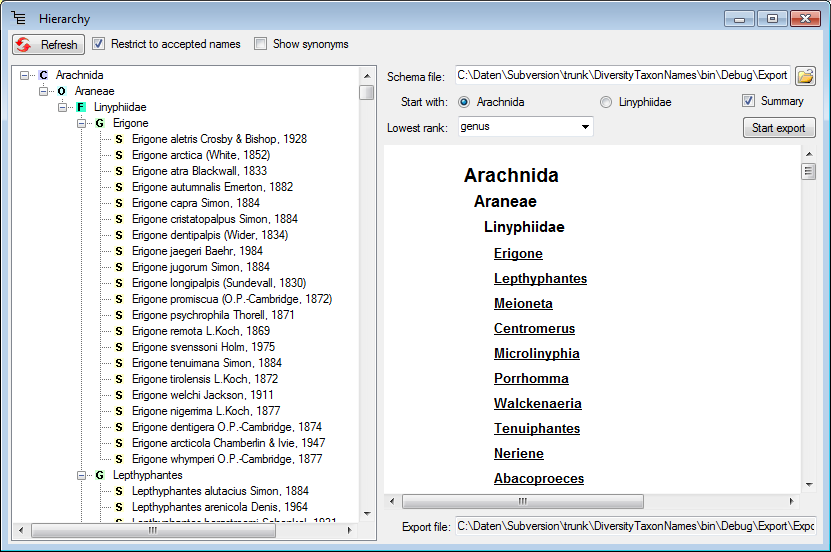
To export only the higher taxa, you can restrict the lowest rank to e.g. the genus as shown below.
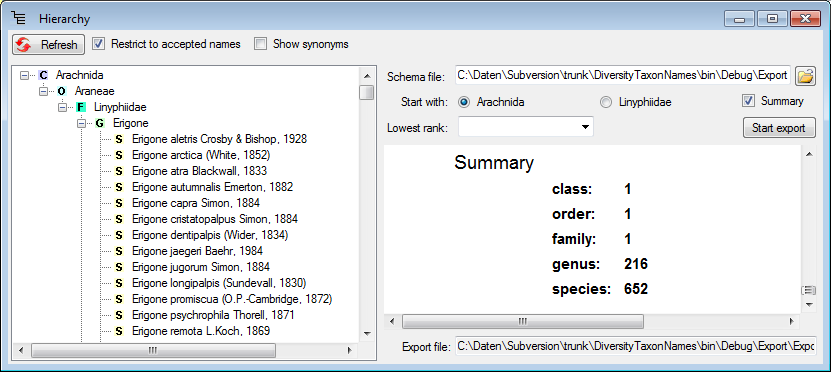
If you choose the option Summary, the numbers of the differnet hierarchical levels will be listed at the bottom of the report (see image below)
To export lists, including information about the distribution or the synonymy, choose Data → Export → Export taxon list … from the menu. A window as shown below will open, where you can choose the taxonomic list and the project where the synonomy of the taxa is documented.
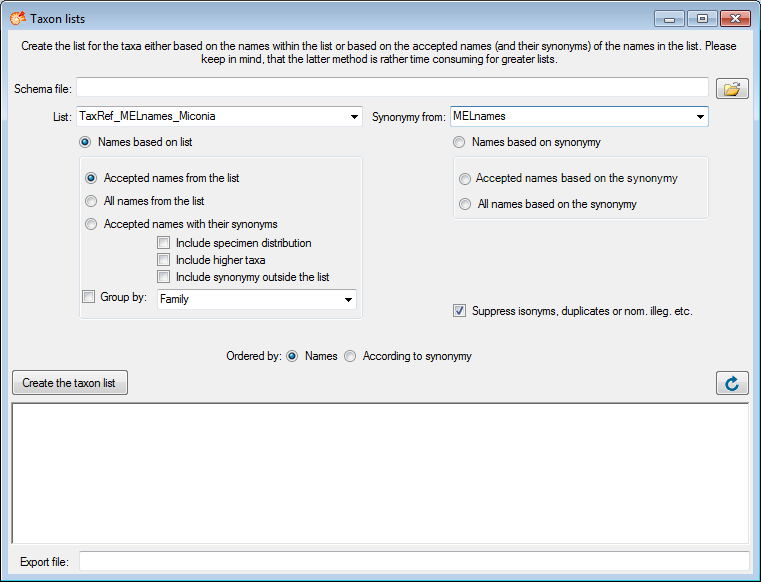
Choose a Schema file and the options for your export. Than click on the Create the taxon list to start the export. The resulting html file (see below) will be named according to the choosen schema file.
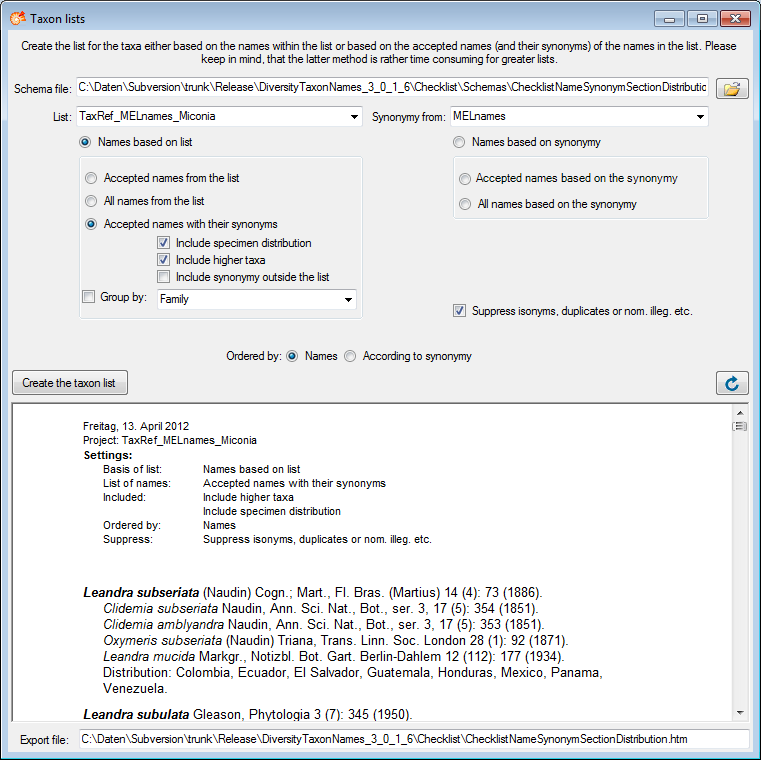
If you miss to
choose a schema file, the original XML file will be shown (see below).
To convert this into a html file, choose a schema file and click the

To export a list of the synonyms for the taxa selected in the query, choose Data → Export → Export synonyms… from the menu. A window as shown below will open. With a click on the button to search for the contents in the database.
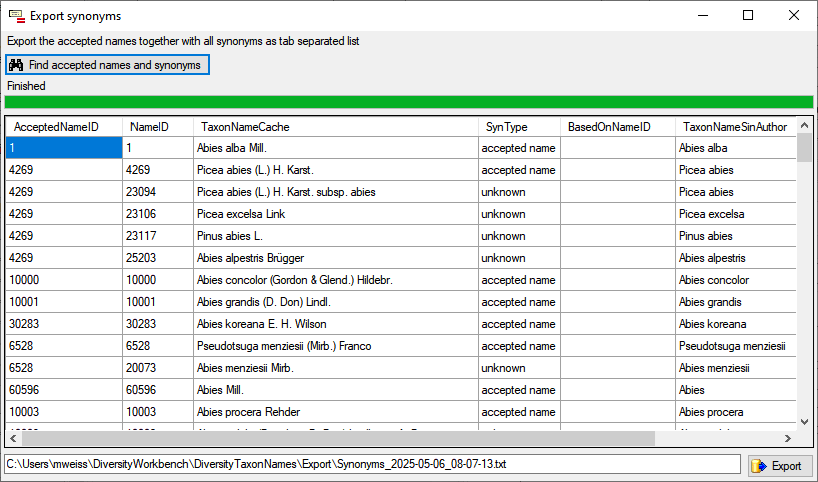
Use the button to export the data from the table to the specified file