Diversity Collection
Queries - overview
Once you are connected to your database, you can search across all data. A wide range of search options is available.
All functions related to querying can be found on the left-hand side of the main window.
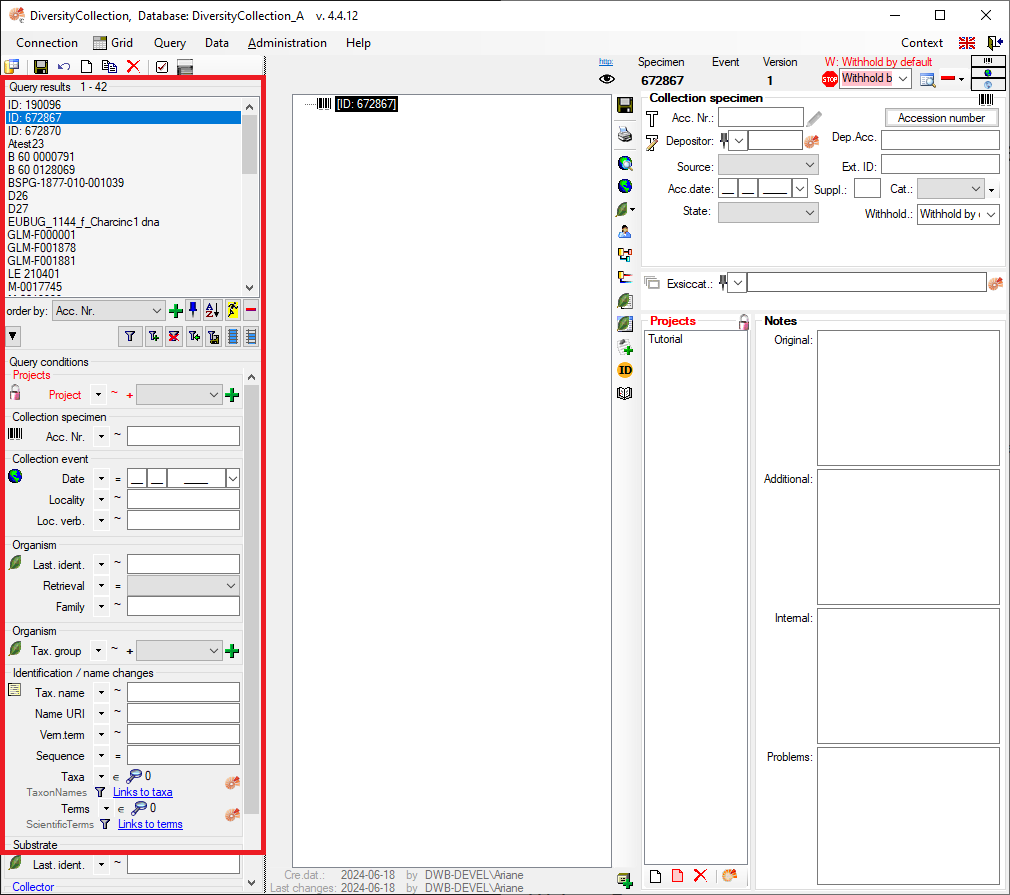
The upper part of the query section contains the list of all results, titled “Query Results”.
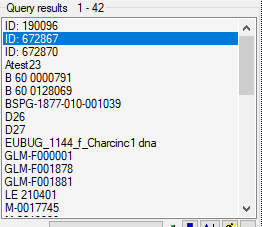
Below this, you will find a section containing all the buttons relevant to the search.
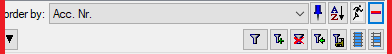
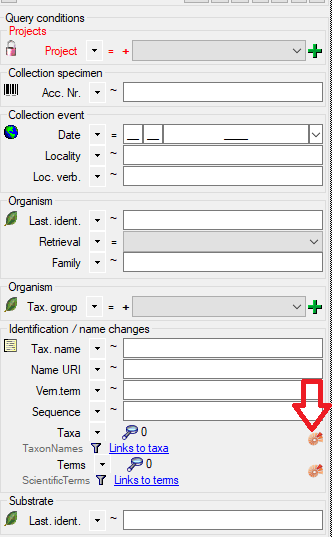
Below the query buttons, you will find the “Query Conditions” section. This is where you can enter all available search criteria.
Display the Entire Dataset
To display the entire dataset, start a search without specifying any criteria in the “Query conditions” section:
-
In the middle of the query section on the left-hand side of the main window, click on the “Filter” button.
-
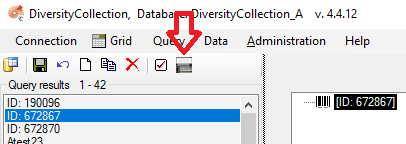
A list of the results will be displayed in the “Query Results” section. The number of results is shown above the list, next to the “Query Results” label.

Filter a Search
Below the query buttons, at the bottom of the query section, you will find the “Query Conditions”.
- Enter the filter criteria for your search. For example, you can select a project from the dropdown list.
- You can combine as many criteria as needed to narrow down your results.
- Start the query by clicking the “Filter” button
 .
.
- A list of results will be displayed in the “Query Results” section. The number of results is shown above the list, next to the “Query Results” label. If no results match the query, the list remains empty and the label “No match” is displayed.
Edit and Customise Query Conditions
You can choose which query conditions are displayed in the main window, and you can change this at any time.
- At the top left, above the query results list, click the “Checkbox” button
 .
.
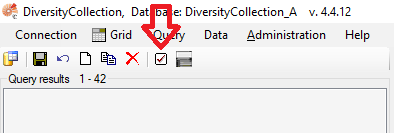
- Select any query conditions you want to use for your searches by selecting the respective checkboxes in the treeview.
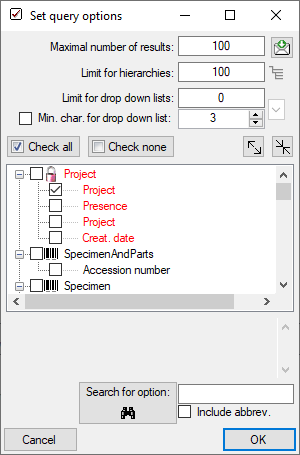
Customise the Interface
Hide/Show the Entire Query Section
In the main window, go to the menu item Query → Show Query.
Hide the “Query Conditions” Section
On the left side of the “Query Buttons”, in the middle of the query section, click the “Arrow” button  .
.
Switch Between Vertical and Horizontal Arrangement
You can change the layout of the query elements from vertical to horizontal and vice versa. To do this, click the button located below the main menu bar:
Edit the Result List
Add Results to the Existing List
You can add new results, based on different query conditions, to your current result list.
- Enter the new filter criteria for your additional search.
- Start the query and add the results to the existing list by clicking the button
 .
.
- The new results will be appended to the existing list.
Remove Result Items from the List
You can remove entries from your current result list:
- Select the entries you want to remove.
- Click the button
 .
.
Important This does not delete the data from the database. It only affects the current display in the results list.
Many Result Columns
The option to display a result list with many columns is described in the
chapter Many Columns.
Query Conditions
Remember the Last Query
By default, the values you entered for the previous query will be remembered. Your query criteria will be pre-filled when the programme starts. To change this behaviour, click the Pin button
 .
.
Query Annotation
The query for annotations differs from a standard query (see below).
In addition, you can specify the type of annotation (Annotation
 , Problem
, Problem  , Reference
, Reference
 ) and the linked table (see
Annotation).
) and the linked table (see
Annotation).
Duplicates
Certain query condition fields allow you to add up to three duplicates of the same condition. For adding a ‘duplicate’ search criteria, click the green “Plus” button  . Remove a ‘duplicate’ search condition with a click on the red “Minus” button
. Remove a ‘duplicate’ search condition with a click on the red “Minus” button  . The restrictions can be combined with AND
. The restrictions can be combined with AND + and OR |. To switch between these modes, click the resp. + or | icon.
Query Modules
In the “Query Conditions” section, some values may be linked to other modules. For example, within the “Identification” group, the fields “Taxa” and “Terms” are linked to the “DiversityTaxonNames” and “DiversityScientificTerms” modules, respectively. You can also add “linked” values to your query condition.
- Select the operator that determines how the entries are used in the search. An explanation of all available operators can be found in the table below.
- To connect to the linked module, click the “Ammonite” button located to the right of the relevant query field.
- A query window for the linked module will open.
- Search for values within the linked module and click “Ok” to confirm your section.
- If you want to view a list of the selected items, click the Magnifying Glass button
 .
.
Info: There is also a detailed  available, which explains all possible operators and how to use them.
available, which explains all possible operators and how to use them.
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| ∈ |
Search for entries with a list |
Rosa | Rosa caninia \ |
| ∉ |
Search for entries not within a list |
Rosa | Rosa caninia | ... |
+H  |
search for entry including lower hierarchy |
Picea | Picea abies | ... |
+S  |
search for entry including synonyms |
Picea abies | Pinus abies | ... |
+HS  |
search for entry including lower hierarchy and synonyms |
Picea | Picea abies | Pinus abies | ... |
 |
Change filter mode between link and text |
http://tnt.diversityworkbench.de/TaxonNames_Plants/4269 <> Picea abies L. |
Videos
- Introduction on how to use the query conditions:

- How to use special query conditions:

- Tutorial on how to query modules:

- Tutorial on how to save a query:
 .
.
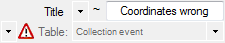
Query any fields
The query for any fields  will search in several
fields, e.g., withholding reasons in specimens, images, etc. There are two
versions: The first version (e.g., Notes) will search in all tables but
not in collection event tables, while the second version (e.g,. Any notes)
will search in any table (see image below).
will search in several
fields, e.g., withholding reasons in specimens, images, etc. There are two
versions: The first version (e.g., Notes) will search in all tables but
not in collection event tables, while the second version (e.g,. Any notes)
will search in any table (see image below).
Subsections of Query
Diversity Collection
Optimized query
To speed up the query you may use the optimized version.
Icons
Standard query:  Optimized query:
Optimized query: 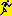
The optimized query in combination with the  remembering option includes the functionality to preselect data
depending on the query restrictions, e.g. if you search for an
identification and enter a taxonomic name the first identification
matching the restrictions will be preselected in the main window as
shown below.
remembering option includes the functionality to preselect data
depending on the query restrictions, e.g. if you search for an
identification and enter a taxonomic name the first identification
matching the restrictions will be preselected in the main window as
shown below.
Default
To set the “optimized query” and the “remember last query” option as default, go to Administration → Customize display in the menu of the main window. In the tab Defaults and miscellaneous select the “Optimized and “Remember” option. The buttons are hidden in the main window, providing more space.

Many columns
The option to include several columns in the result list is only
available for optimized queries  . To display
several columns in the result list, click on the
. To display
several columns in the result list, click on the  button next to the order by column (see below). A window will open where
you can select the next column for the sorting. Underneath the order by
column the second column for the sorting will be added. To remove this
sorting column you can click on the
button next to the order by column (see below). A window will open where
you can select the next column for the sorting. Underneath the order by
column the second column for the sorting will be added. To remove this
sorting column you can click on the  button. By
default the width for the columns is set to 10. You can change this
according to content. To set the width to the maximal length of the
current content, click on the
button. By
default the width for the columns is set to 10. You can change this
according to content. To set the width to the maximal length of the
current content, click on the  button.
To change the sorting of the added order column click on the
button.
To change the sorting of the added order column click on the
 button. The colums are separated via "
| " as shown in the image below.
button. The colums are separated via "
| " as shown in the image below.
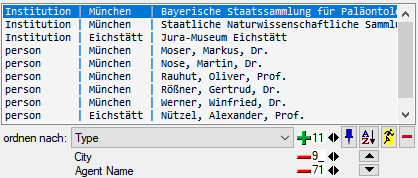
For an introduction see the videos:
- Mehrspaltige Suche:

- Sortierung:

Diversity Collection

Predefined queries
Besides setting queries for specimens via the query options you may
define separate predefined user-specific queries. These are listed in
the menu topic Query - Predefined queries.
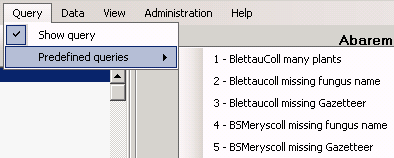
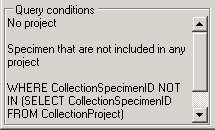
If you choose one of these predefined queries, the query options will be
hidden and the command of the query will be shown at the base of the
specimen list. The first line shows the title of the
query, the next lines contain the description followed by the part of
the query command which restricts the selection of the data sets (=
WHERE-clause of the SQL-statement).
To return to the user-defined query click on the Show
query conditions  button.
button.
If you are an administrator, you may create new queries for users. To
create a predefined query choose Administration - Queries... from
the menu. A window will open as shown below, where you may create, edit
and test your queries.
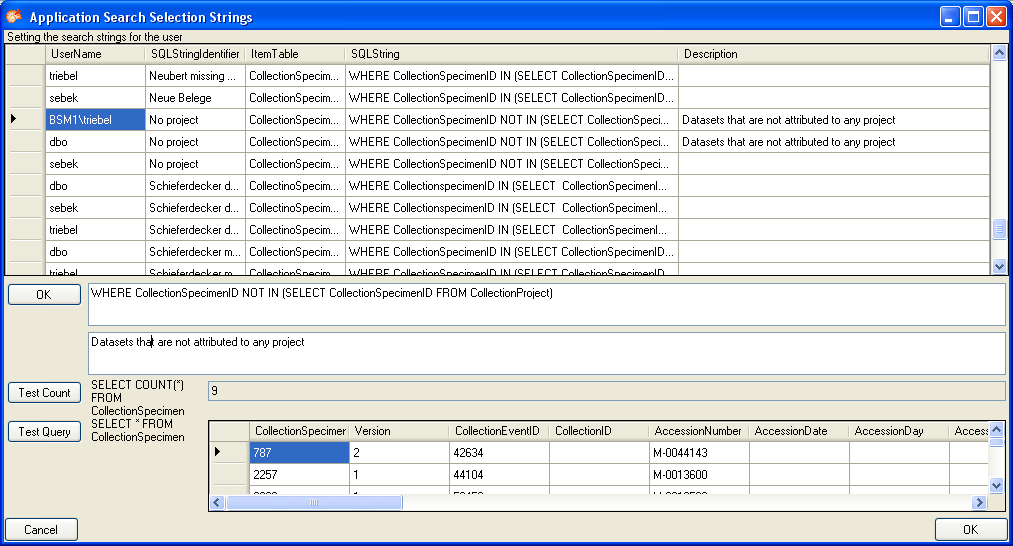
In the upper field you define the WHERE-clause of the SQL string of your
query. Keep in mind that the queries can refer to different tables,
depending on the order column chosen by the user. Thus, queries in
DiversityCollection should start with the reference to the primary key
of the main table (CollectionSpecimenID in table CollectionSpecimen and
depending tables). The lower field contains the description for the
query as shown in the user interface. To test a query use the Test count and Test query buttons.
Diversity Collection
Query Operators
When entering your query conditions, you have various operators to choose from.
The available operators are shown in the tables below.
Availability: t = text, n = numeric, d = date, h = hierarchy, x = XML, e
= EXIF, g = geography, a = annotation, m = module\
| Op. |
Meaning |
Example |
Avail. |
| ∼ |
search for an entry like… (you may use wildcards) |
Pinus s[iy]lvestris % |
tn---e-- |
| = |
search for an entry exactly equal to … |
Pinus silvestris L. |
tndh---- |
| ≠ |
search for an entry not like... |
Pinus s[iy]lvestris % (you may use wildcards) |
tn------ |
| ∅ |
search for an entry where a value is missing … |
|
tndhxeg- |
| • |
search for an entry where a value is present … |
|
tndhxeg- |
| - |
search for an entry between … and … |
2000 - 2003 |
tnd----- |
| | |
search within a list of entries, separated by "|" or one line per value. If wildcards ("%", "_") are included the query will search for values like the given values |
2000 | 2003 ... | 2000 2003 |
tn------ |
| ∈ |
search with exclusion of a list of entries with one value per line. Wildcards will be ignored |
2000 2003 |
tn—–m |
| ∉ |
search with exclusion of a list of entries with one value per line. Wildcards will be ignored |
2000 2003 |
tn—–m |
| ± |
search for an entry where only parts of the date are present… |
-.-.2006 |
--d----- |
| Δ |
search including children in a hierarchy … |
M-Fungi |
---h---- |
| / |
Search for entries containing a given XML node (not for EXIF) |
settings |
----x--- |
| ¬ |
Search for entries not containing a given XML node (not for EXIF) |
settings |
----x--- |
| ‡ |
Search for entries with a maximal distance of … |
POINT(24.24 45.243) | 50 km |
------g- |
| O |
Search for entries within an area |
POLYGON(34.5 ... |
------g- |
| ¤ |
Search for entries outside an area |
POLYGON(34.5 ... |
------g- |
| +H |
Search for entry including lower hierarchy |
Picea | Picea abies |
-------m |
| +S |
Search for entry including synonyms |
Picea abies | Pinus abies |
-------m |
| +HS |
Search for entry including lower hierarchy and symonyms |
Picea | Picea abies | Pinus abies |
-------m |
Operators for datasets
| Operator |
Meaning |
| ∅ |
search for missing datasets ... |
| • |
search for existing datasets ... |
Operators for text
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| ∼ |
search for an entry like ... |
Pinus s[iy]lvestris % (you may use wildcards) |
| = |
search for an entry exactly equal to ... |
Pinus silvestris L. |
| ≠ |
search for an entry not like ... |
Pinus s[iy]lvestris% (you may use wildcards) |
| ∅ |
search for an entry where a value is missing ... |
|
| • |
search for an entry where a value is present ... |
|
| - |
search for an entry between ... and ... |
2000 - 2003 |
| | |
search within a list of entries, separated by "|" or one line per value. If wildcards ("%", "_") are included the query will search for values like the given values |
2000 | 2003 ... | 2000 2003 |
| ∈ |
search with exclusion of a list of entries with one value per line. Wildcards will be ignored |
2000 2003 |
| ∉ |
search with exclusion of a list of entries with one value per line. Wildcards will be ignored |
2000 2003 |
Operators for numeric data
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| = |
search for an entry exactly equal to … |
Pinus silvestris L. |
| < |
search for an entry lower than ... |
2006 |
| > |
search for an entry higher than ... |
2006 |
| - |
search for an entry between ... and ... |
2000 - 2003 |
| | |
search within a list of entries, separated by "|" or one line per value |
2000 | 2003 |
| ∈ |
search within a list of entries with one value per line |
2000 2003 |
| ∉ |
search with exclusion of a list of entries with one value per line |
2000 2003 |
| ∅ |
search for an entry where a value is missing ... |
|
| • |
search for an entry where a value is present |
|
Operators for date values
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| = |
search for an entry exactly equal to ... |
20.3.2006 |
| < |
search for an entry lower than ... |
20.3.2006 |
| > |
search for an entry higher than ... |
20.3.2006 |
| - |
search for an entry between two dates... |
20.3.2006 - 29.3.2006 |
| ± |
search for an entry where only parts of the date are present... |
-.-.2006 |
| ∅ |
search for an entry where the date is missing … |
|
| • |
search for an entry where the date is present and complete … |
|
Oparators for hierachy
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| = |
search for an entry exactly equal to ... |
M-Fungi |
| ≠ |
search for an entry which is not equal to … |
M-Fungi |
| ∅ |
search for missing entry ... |
|
| • |
search for present entry ... |
|
| Δ |
search including children in a hierarchy ... |
M-Fungi |
Operators for XML
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| ~ |
Search for entries like a given text (for EXIF) |
RDF |
| / |
Search for entries containing a given XML node (not for EXIF) |
settings |
| ¬ |
Search for entries not containing agiven XML node (not for EXIF) |
settings |
| ∅ |
search for missing entry ... |
|
| • |
search for present entry ... |
|
Operators for geography
Use (via local files or manual creation) resp. (via DiversityGazetteer) button to set geography
| Operator |
Meaning |
Example |
| ‡ |
Search for entries with a maximal distance of ... |
POINT(24.24 45.243) | 50 km |
| O |
Search for entries within an area |
POLYGON(34.5 ... |
| ¤ |
Search for entries outside an area |
POLYGON(34.5 ... |
| ∅ |
search for missing entry... |
|
| • |
search for present entry ... |
|
For yes/no fields exists a checkbox with 3 options:
 = yes,
= yes, 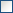 = no,
= no,
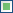 = undefined
= undefined
For a search within a lists (using the |, ∈ or ∉ operator) you may
double click in the text field to open a window where you can enter your
values. To separate the values either use the "|" sign or a new line
as shown in the image below.

Wildcards in SQL
There are 4 different possibilities for wildcards in SQL:
| Operator |
Description |
Example |
Result |
| % |
any string consisting of no, one or many characters |
Pinus % |
will find anything like Pinus, Pinus sylvestris, Pinus strobus etc. |
| * |
same effect as % (see above) |
|
|
| _ |
a single character |
Pinus s_lvestris |
will find Pinus sylvestris and Pinus silvestris etc. |
| […] |
any character out of a given range like [abcde] or [a-e] |
Pinus s[iy]lvestris |
will find Pinus sylvestris and Pinus silvestris |
| [^…] |
any character not in a given range like [^abcde] or [^a-e] |
Pinus s[^i]lvestris |
will find Pinus sylvestris but not Pinus silvestris |
Diversity Collection
Saved queries
Save query
If you wish to save a current query, click on the  button. A window will open as shown below where you may specify the
title and description of you query.
button. A window will open as shown below where you may specify the
title and description of you query.
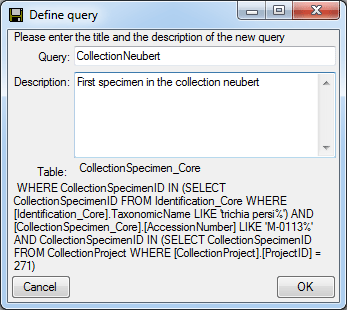
After you entered title and description of the query, click OK to
specify the query group. A window will open as shown below. Standard
queries are symbolized with an  icon while
optimized queries are symbolized with an
icon while
optimized queries are symbolized with an  icon and yellow background (see below).
icon and yellow background (see below).
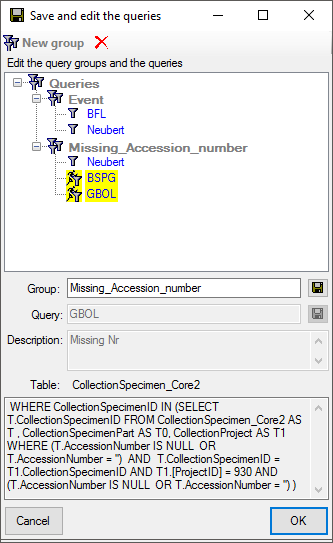
Choose a group from the tree or create a new one and click OK. The new
query will be included in the selected group.
Finally, you may edit the titles and descriptions of the groups and
queries. Click the  save button to store the changes. To
delete items from the tree select the item and click on the
save button to store the changes. To
delete items from the tree select the item and click on the
 button. Click OK to save the new query and close
the window.
button. Click OK to save the new query and close
the window.
Load query
If you wish to load a query which has been stored previously, click on
the  button. A window will open as shown
below. Please note that if the optimizer
button. A window will open as shown
below. Please note that if the optimizer
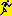 is activated, only the queries created with
the optimizer are available (not optimized queries are disabled).
is activated, only the queries created with
the optimizer are available (not optimized queries are disabled).
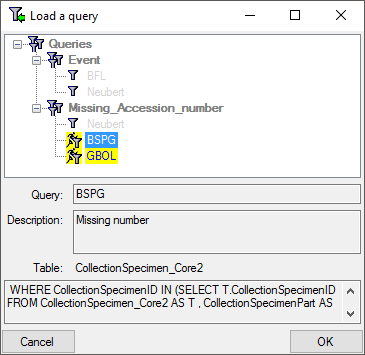
For not optimized queries, the optimized queries will be disabled as
shown below.
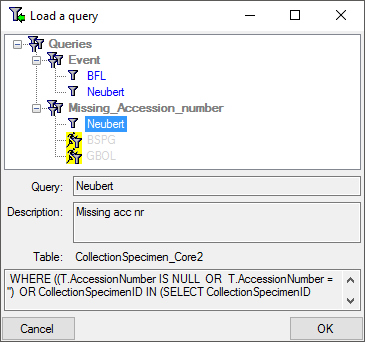
Choose a query from the tree and click OK to close the form and filter
the data sets according to the selected query.
Diversity Collection
Query Wildcards
Wildcards in SQL
There are 4 different possibilities for wildcards in SQL:
| Operator |
Description |
Example |
Result |
| % |
any string consisting of no, one or many characters |
Pinus % |
will find anything like Pinus, Pinus sylvestris, Pinus strobus etc. |
| * |
same effect as % (see above) |
|
|
| _ |
a single character |
Pinus s_lvestris |
will find Pinus sylvestris and Pinus silvestris etc. |
| […] |
any character out of a given range like [abcde] or [a-e] |
Pinus s[iy]lvestris |
will find Pinus sylvestris and Pinus silvestris |
| [^…] |
any character not in a given range like [^abcde] or [^a-e] |
Pinus s[^i]lvestris |
will find Pinus sylvestris but not Pinus silvestris |
Scan mode
Scanner
With the scan mode you may use a barcode scanner or the camera of your
computer or tablet using e.g.
bcWebCam to search for a
specimen. To work with the scan mode select the Scan mode in the
Query menu. The query part will be hidden and the field for the
scanned identifier will be accessible for the entry via the scanner. As
possible identifiers you can choose among the accession number of the
specimen  , the ID of the specimen ID, the
accession number of the part
, the ID of the specimen ID, the
accession number of the part  or the
identifier of the organism
or the
identifier of the organism  . If the field
for the entry of the identifier
. If the field
for the entry of the identifier  is not
activated, move the mouse to the field to activate it. Once you scan the
barcode the program will start the search for the specimen in the
database. To return to another query mode deselect the Scan mode.
is not
activated, move the mouse to the field to activate it. Once you scan the
barcode the program will start the search for the specimen in the
database. To return to another query mode deselect the Scan mode.
If the results captured by the scanner do not correspond to the scanned
codes, the timer intervall may need an adaption to your scanner.
To set the timer interval of the scanner, click on the
 button. The default is set to 200 ms. Change it
until the results captured by the scanner correspond to the codes.
button. The default is set to 200 ms. Change it
until the results captured by the scanner correspond to the codes.

The second scan mode  for collection
codes (stable identifier for collections) or
the name of the collection will list all specimen
within a collection. For the query of collection names these must be
unique within the database. The query for collections may include
depending collections. By default only specimen of the selected
collection will be shown. Click on the
for collection
codes (stable identifier for collections) or
the name of the collection will list all specimen
within a collection. For the query of collection names these must be
unique within the database. The query for collections may include
depending collections. By default only specimen of the selected
collection will be shown. Click on the  button above the
button above the  button to change to
the
button to change to
the  mode including specimen in depending
collections.
mode including specimen in depending
collections.
Diversity Collection
Queries - many columns
The option to include several columns in the result list is only
available for optimized queries 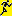 . To display
several columns in the result list, click on the
. To display
several columns in the result list, click on the  button next to the order by column (see below). A window will open where
you can select the next column for the sorting. Underneath the order by
column the second column for the sorting will be added. To remove this
sorting column you can click on the
button next to the order by column (see below). A window will open where
you can select the next column for the sorting. Underneath the order by
column the second column for the sorting will be added. To remove this
sorting column you can click on the  button. By
default the width for the columns is set to 10. You can change this
according to content. To set the width to the maximal length of the
current content, click on the
button. By
default the width for the columns is set to 10. You can change this
according to content. To set the width to the maximal length of the
current content, click on the  button.
To change the sorting of the added order column click on the
button.
To change the sorting of the added order column click on the
 button. The colums are separated via "
| " as shown in the image below.
button. The colums are separated via "
| " as shown in the image below.

For an introduction see the videos:
- Mehrspaltige Suche:

- Sortierung:

Diversity Collection
Result list
The result list displays the specimens found in a query.
The specimens may be displayed with their e.g. with their accession
number. To change the information of the specimen shown in the list,
choose among the option provided in the order by: combobox.
Some possibilities are shown above: identifications, storage location or
collectors number. After you changed the selection of the displayed
information, you have to start the query  to see
it in the result list. To view further information on the chosen field
simply place the mouse in the field. A text box will appear with the
description of the field (see below).
to see
it in the result list. To view further information on the chosen field
simply place the mouse in the field. A text box will appear with the
description of the field (see below).

You may restrict the maximum number of specimens and queryoptions (click on the  button), if you have for example a slow connection to the database. As a
default the maximum number is set to 100. If the number of data sets
according to your query is higher than the maximum value set in the
query options, it will be indicated in the header of the list.
button), if you have for example a slow connection to the database. As a
default the maximum number is set to 100. If the number of data sets
according to your query is higher than the maximum value set in the
query options, it will be indicated in the header of the list.
To ensure that restrictions set in the query conditions will be applied
to the specimen list make sure that you choose matching restrictions and
order columns as shown below. In the upper example corresponding fields
were used for restricting the query and the display (Tax. name).
Here the query results will be restricted to said field.
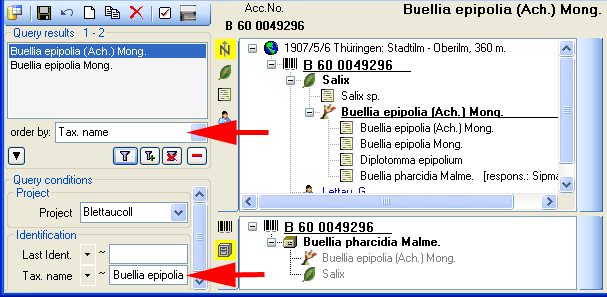
In the second example a different field for the restriction was chosen
(Last ident. <> Tax. name). The query result in consequence
will list all data sets with entries found in the field Tax. name
and entries which match the restriction (see below).
To search for specimens enter the restrictions in the fields for the
search conditions and click on the  filter button. The
specimens found in the database will be shown in the result list. To add
specimens with differing search conditions click on the
filter button. The
specimens found in the database will be shown in the result list. To add
specimens with differing search conditions click on the
 button. If the list of items is longer than
your maximum number of returned items you may browse the next items with
the
button. If the list of items is longer than
your maximum number of returned items you may browse the next items with
the  button. If you wish to remove entries from
the selected list, choose them in the list and click on the
button. If you wish to remove entries from
the selected list, choose them in the list and click on the
 button. This will not
delete the data from the database but remove them from your query
result.
button. This will not
delete the data from the database but remove them from your query
result.
The result list will contain data with Read
only access. For these data
all controls and menus for editing the data will be disabled except the
button for adding annotations  .
.
Here are some examples you may select for display in the result list:
AccessionNumber: One entry is shown for each specimen
with its corresponding accession number.
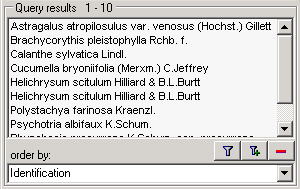
Last identification: The last identification for
every unit in a specimen is shown in the list. As there can be several
units in one specimen, several entries for one specimen may appear in
the list.
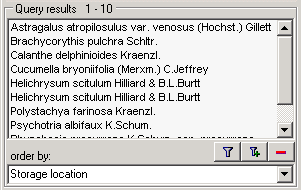
Storage location: The storage location of every part of a
specimen stored in the collections is shown in the list. As parts of a
specimen can be stored in several collections under different names,
several entries for one specimen may appear in the list.
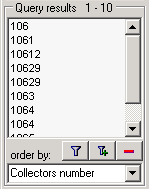
Collecting number: The collecting number given by the
collector of every sample of a specimen is shown in the list. A specimen
may have several collectors each with a different number. Therefore,
several entries for one collection specimen may appear in the list.






.
.




.
.








.





.


 Optimized query:
Optimized query: 

 . To display
several columns in the result list, click on the
. To display
several columns in the result list, click on the  button.
To change the sorting of the added order column click on the
button.
To change the sorting of the added order column click on the




 button.
button.
 = yes,
= yes,  = no,
= no,
 = undefined
= undefined
 button. A window will open as shown below where you may specify the
title and description of you query.
button. A window will open as shown below where you may specify the
title and description of you query.
 icon and yellow background (see below).
icon and yellow background (see below).
 button. A window will open as shown
below. Please note that if the
button. A window will open as shown
below. Please note that if the 


 , the ID of the specimen ID, the
accession number of the part
, the ID of the specimen ID, the
accession number of the part  or the
identifier of the organism
or the
identifier of the organism  . If the field
for the entry of the identifier
. If the field
for the entry of the identifier 
 for collection
codes (
for collection
codes ( button above the
button above the  mode including specimen in depending
collections.
mode including specimen in depending
collections.



 button. If you wish to remove entries from
the selected list, choose them in the list and click on the
button. If you wish to remove entries from
the selected list, choose them in the list and click on the
 .
.


